Page 217 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 217
8.5 Heterogeneous Catalysis: Kinetics in Porous Catalyst Particles 199
Gas film
Bulk
gas
/I
:
I
\
\
Exothermic
CA T
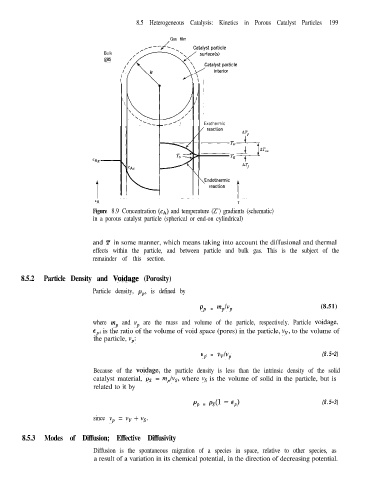
Figure 8.9 Concentration (CA) and temperature (Z’) gradients (schematic)
in a porous catalyst particle (spherical or end-on cylindrical)
and T in some manner, which means taking into account the diffusional and thermal
effects within the particle, and between particle and bulk gas. This is the subject of the
remainder of this section.
8.5.2 Particle Density and Voidage (Porosity)
Particle density, pP, is defined by
pp = m,lv, (8.51)
where mp and I.‘,, are the mass and volume of the particle, respectively. Particle voidage,
ep, is the ratio of the volume of void space (pores) in the particle, I+,, to the volume of
the particle, vp:
EP = v,Iv, (8.5-2)
Because of the voidage, the particle density is less than the intrinsic density of the solid
catalyst material, ps = mplvs, where vS is the volume of solid in the particle, but is
related to it by
PP = P,(l - EP> (8.5-3)
since vp = V” + vs.
8.5.3 Modes of Diffusion; Effective Diffusivity
Diffusion is the spontaneous migration of a species in space, relative to other species, as
a result of a variation in its chemical potential, in the direction of decreasing potential.