Page 271 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 271
252 Chapter 9: Multiphase Reacting Systems
and, for a second-order reaction,
Ha = (kADAC~n)1’21kAe (TZ = 2) (9.2-54)
0 For given values of Ha and Ei, E may be calculated by solving equations 9.2-51 and -52
1
numerically using the E-Z Solve software (or by trial). The results of such calculations
“O-T
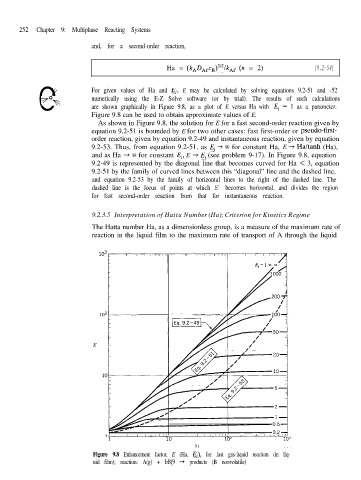
are shown graphically in Figure 9.8, as a plot of E versus Ha with E, -
Figure 9.8 can be used to obtain approximate values of E. 1 as a parameter.
As shown in Figure 9.8, the solution for E for a fast second-order reaction given by
equation 9.2-51 is bounded by E for two other cases: fast first-order or pseudo-first-
order reaction, given by equation 9.2-49 and instantaneous reaction, given by equation
9.2-53. Thus, from equation 9.2-51, as Ei -+ 03 for constant Ha, E + Ha/tanh (Ha),
and as Ha + ~0 for constant Ei, E -+ Ei (see problem 9-17). In Figure 9.8, equation
9.2-49 is represented by the diagonal line that becomes curved for Ha < 3, equation
9.2-51 by the family of curved lines between this “diagonal” line and the dashed line,
and equation 9.2-53 by the family of horizontal lines to the right of the dashed line. The
dashed line is the locus of points at which E becomes horizontal, and divides the region
for fast second-order reaction from that for instantaneous reaction.
9.2.3.5 Interpretation of Hatta Number (Ha); Criterion for Kinetics Regime
The Hatta number Ha, as a dimensionless group, is a measure of the maximum rate of
reaction in the liquid film to the maximum rate of transport of A through the liquid
- - ^^--~..-
Ha
Figure 9.8 Enhancement factor, E (Ha, Ei), for fast gas-liquid reaction (in liq-
uid film); reaction: A(g) + bB(9 --f products (B nonvolatile)