Page 115 - Know and Understand Centrifugal Pumps
P. 115
Know and Understand Centrifugal Pumps
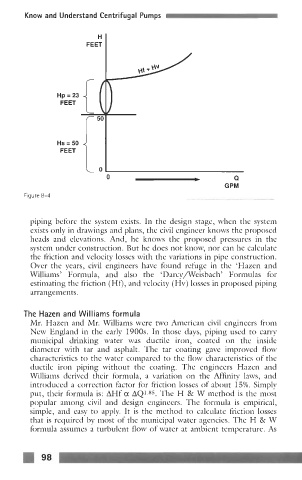
FEET I
H
Hp = 23
FEET
HS = 50
FEET
piping before the system exists. In the design stage, when the system
exists only in drawings and plans, the civil engineer knows the proposed
heads and elevations. And, he knows the proposed pressures in the
system under construction. But he does not know, nor can he calculate
the friction and velocity losses with the variations in pipe construction.
Over the years, civil engineers have found refuge in the ‘Hazen and
Williams’ Formula, and also the ‘Darcy/Weisbach’ Formulas for
estimating the friction (Hf), and velocity (Hv) losses in proposed piping
arrangements.
The Hazen and Williams formula
Mr. Hazen and Mr. Williams were two American civil engineers from
New England in the early 1900s. In those days, piping used to carry
municipal drinking water was ductile iron, coated on the inside
diameter with tar and asphalt. The tar coating gave improved flow
characteristics to the water compared to the flow characteristics of the
ductile iron piping without the coating. The engineers Hazen and
Williams derived their formula, a variation on the Affinity laws, and
introduced a correction factor for friction losses of about 15%. Simply
put, their formula is: AHf a AQl.85. The H & W method is the most
popular among civil and design engineers. The formula is empirical,
simple, and easy to apply. It is the method to calculate friction losses
that is required by most of the municipal water agencies. The H & W
formula assumes a turbulent flow of water at ambient temperature. As
F1 98