Page 21 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 21
Time Scales of Observation and
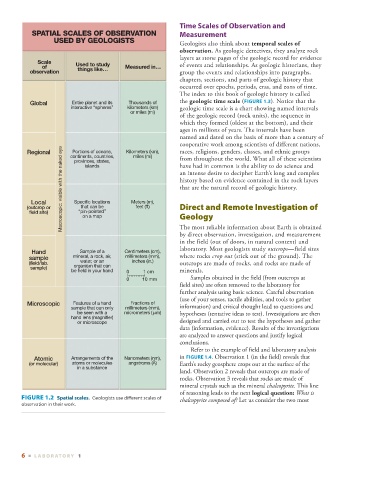
SPATIAL SCALES OF OBSERVATION Measurement
USED BY GEOLOGISTS
Geologists also think about temporal scales of
observation . As geologic detectives, they analyze rock
layers as stone pages of the geologic record for evidence
Scale Used to study
of Measured in… of events and relationships. As geologic historians, they
observation things like… group the events and relationships into paragraphs,
chapters, sections, and parts of geologic history that
occurred over epochs, periods, eras, and eons of time.
The index to this book of geologic history is called
Global Entire planet and its Thousands of the geologic time scale ( FIGURE 1.3 ). Notice that the
interactive “spheres” kilometers (km) geologic time scale is a chart showing named intervals
or miles (mi)
of the geologic record (rock units), the sequence in
which they formed (oldest at the bottom), and their
ages in millions of years. The intervals have been
named and dated on the basis of more than a century of
cooperative work among scientists of different nations,
Macroscopic: visible with the naked eye an intense desire to decipher Earth’s long and complex
Portions of oceans,
Regional continents, countries, Kilometers (km), races, religions, genders, classes, and ethnic groups
miles (mi)
from throughout the world. What all of these scientists
provinces, states,
have had in common is the ability to do science and
islands
history based on evidence contained in the rock layers
that are the natural record of geologic history.
Local Specific locations Meters (m),
(outcrop or that can be feet (ft) Direct and Remote Investigation of
field site) “pin-pointed” Geology
on a map
The most reliable information about Earth is obtained
by direct observation, investigation, and measurement
in the field (out of doors, in natural context) and
laboratory. Most geologists study outcrops —field sites
Hand Sample of a Centimeters (cm),
sample mineral, a rock, air, millimeters (mm), where rocks crop out (stick out of the ground). The
(field/lab. water, or an inches (in.) outcrops are made of rocks, and rocks are made of
sample) organism that can
be held in your hand 0 1 cm minerals.
0 10 mm Samples obtained in the field (from outcrops at
field sites) are often removed to the laboratory for
further analysis using basic science. Careful observation
(use of your senses, tactile abilities, and tools to gather
Microscopic Features of a hand Fractions of
sample that can only millimeters (mm), information) and critical thought lead to questions and
be seen with a micrometers ( m) hypotheses (tentative ideas to test). Investigations are then
hand lens (magnifier)
or microscope designed and carried out to test the hypotheses and gather
data (information, evidence). Results of the investigations
are analyzed to answer questions and justify logical
conclusions.
Refer to the example of field and laboratory analysis
Atomic Arrangements of the Nanometers (nm), in FIGURE 1.4 . Observation 1 (in the field) reveals that
(or molecular) atoms or molecules angstroms (Å) Earth’s rocky geosphere crops out at the surface of the
in a substance
land. Observation 2 reveals that outcrops are made of
rocks. Observation 3 reveals that rocks are made of
mineral crystals such as the mineral chalcopyrite . This line
of reasoning leads to the next logical question : What is
FIGURE 1.2 Spatial scales. Geologists use different scales of chalcopyrite composed of? Let us consider the two most
observation in their work.
6 ■ L ABOR ATORY 1