Page 216 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 216
202 LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT HANDBOOK
Fabricated uranium (in the form of U0 2) is then transferred to the nuclear
plant. The output thermal and electrical energy from the nuclear plant is input
to the hydrogen plant, and the product of the hydrogen plant is hydrogen fuel.
Various Cu-Cl cycles for thermochemical water decomposition have been
identified and described in the literature. These are characterized by the num-
ber of major chemical steps they incorporate. Although all Cu-Cl thermochem-
ical cycles consist of a series of chemical reactions, the net reaction for each is
water decomposition:
H 2 0(g)^H 2 (g) + l/20 2 (g) (8.4)
Hence water, thermal energy and electricity are the external inputs during
operation of the Cu-Cl thermochemical cycle, and oxygen and hydrogen are
the outputs.
Data used in the analyses are obtained from the literature and normalization
procedures are applied.
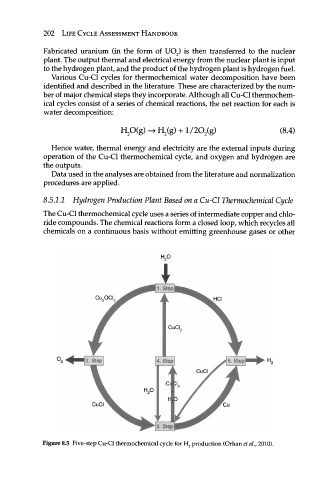
851.1 Hydrogen Production Plant Based on a Cu-Cl Thermochemical Cycle
The Cu-Cl thermochemical cycle uses a series of intermediate copper and chlo-
ride compounds. The chemical reactions form a closed loop, which recycles all
chemicals on a continuous basis without emitting greenhouse gases or other
H o0
0 0
Figure 8.5 Five-step Cu-Cl thermochemical cycle for H 2 production (Orhan et al, 2010).