Page 264 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 264
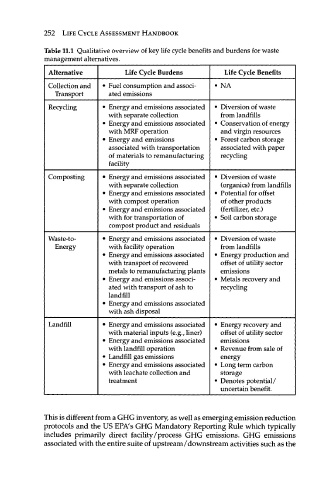
252 LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT HANDBOOK
Table 11.1 Qualitative overview of key life cycle benefits and burdens for waste
management alternatives.
Alternative Life Cycle Burdens Life Cycle Benefits
Collection and • Fuel consumption and associ- • NA
Transport ated emissions
Recycling • Energy and emissions associated • Diversion of waste
with separate collection from landfills
• Energy and emissions associated • Conservation of energy
with MRF operation and virgin resources
• Energy and emissions • Forest carbon storage
associated with transportation associated with paper
of materials to remanufacturing recycling
facility
Composting • Energy and emissions associated • Diversion of waste
with separate collection (organics) from landfills
• Energy and emissions associated • Potential for offset
with compost operation of other products
• Energy and emissions associated (fertilizer, etc.)
with for transportation of • Soil carbon storage
compost product and residuals
Waste-to- • Energy and emissions associated • Diversion of waste
Energy with facility operation from landfills
• Energy and emissions associated • Energy production and
with transport of recovered offset of utility sector
metals to remanufacturing plants emissions
• Energy and emissions associ- • Metals recovery and
ated with transport of ash to recycling
landfill
• Energy and emissions associated
with ash disposal
Landfill • Energy and emissions associated • Energy recovery and
with material inputs (e.g., liner) offset of utility sector
• Energy and emissions associated emissions
with landfill operation • Revenue from sale of
• Landfill gas emissions energy
• Energy and emissions associated • Long term carbon
with leachate collection and storage
treatment • Denotes potential/
uncertain benefit.
This is different from a GHG inventory, as well as emerging emission reduction
protocols and the US EPA's GHG Mandatory Reporting Rule which typically
includes primarily direct facility/process GHG emissions. GHG emissions
associated with the entire suite of upstream/downstream activities such as the