Page 74 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 74
60 N. E. Korres
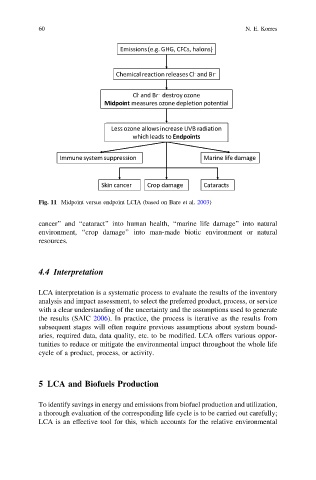
Fig. 11 Midpoint versus endpoint LCIA (based on Bare et al. 2003)
cancer’’ and ‘‘cataract’’ into human health, ‘‘marine life damage’’ into natural
environment, ‘‘crop damage’’ into man-made biotic environment or natural
resources.
4.4 Interpretation
LCA interpretation is a systematic process to evaluate the results of the inventory
analysis and impact assessment, to select the preferred product, process, or service
with a clear understanding of the uncertainty and the assumptions used to generate
the results (SAIC 2006). In practice, the process is iterative as the results from
subsequent stages will often require previous assumptions about system bound-
aries, required data, data quality, etc. to be modified. LCA offers various oppor-
tunities to reduce or mitigate the environmental impact throughout the whole life
cycle of a product, process, or activity.
5 LCA and Biofuels Production
To identify savings in energy and emissions from biofuel production and utilization,
a thorough evaluation of the corresponding life cycle is to be carried out carefully;
LCA is an effective tool for this, which accounts for the relative environmental