Page 327 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 327
326 15. Barriers identification and prioritization
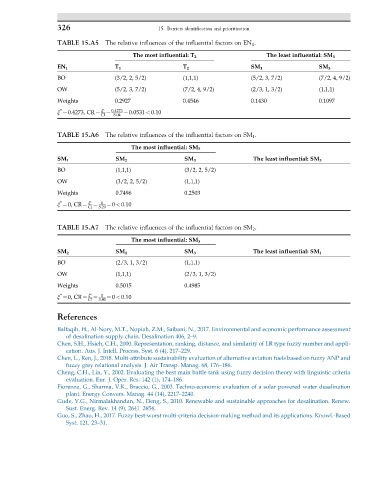
TABLE 15.A5 The relative influences of the influential factors on EN 1 .
The most influential: T 2 The least influential: SM 3
EN 1 T 1 T 2 SM 1 SM 3
BO (3/2, 2, 5/2) (1,1,1) (5/2, 3, 7/2) (7/2, 4, 9/2)
OW (5/2, 3, 7/2) (7/2, 4, 9/2) (2/3, 1, 3/2) (1,1,1)
Weights 0.2927 0.4546 0.1430 0.1097
∗ ξ ∗ 0:4273
ξ ¼0.4273, CR ¼ ¼ ¼ 0:0531 < 0:10
CI 8:04
TABLE 15.A6 The relative influences of the influential factors on SM 1 .
The most influential: SM 2
SM 1 SM 2 SM 3 The least influential: SM 3
BO (1,1,1) (3/2, 2, 5/2)
OW (3/2, 2, 5/2) (1,1,1)
Weights 0.7496 0.2503
∗ ξ ∗ 0
ξ ¼0, CR ¼ ¼ ¼ 0 < 0:10
CI 5:29
TABLE 15.A7 The relative influences of the influential factors on SM 2 .
The most influential: SM 3
SM 2 SM 1 SM 3 The least influential: SM 1
BO (2/3, 1, 3/2) (1,1,1)
OW (1,1,1) (2/3, 1, 3/2)
Weights 0.5015 0.4985
∗ ξ ∗ 0
ξ ¼0, CR ¼ ¼ ¼ 0 < 0:10
CI 3:80
References
Balfaqih, H., Al-Nory, M.T., Nopiah, Z.M., Saibani, N., 2017. Environmental and economic performance assessment
of desalination supply chain. Desalination 406, 2–9.
Chen, S.H., Hsieh, C.H., 2000. Representation, ranking, distance, and similarity of LR type fuzzy number and appli-
cation. Aus. J. Intell. Process. Syst. 6 (4), 217–229.
Chen, L., Ren, J., 2018. Multi-attribute sustainability evaluation of alternative aviation fuels based on fuzzy ANP and
fuzzy grey relational analysis. J. Air Transp. Manag. 68, 176–186.
Cheng, C.H., Lin, Y., 2002. Evaluating the best main battle tank using fuzzy decision theory with linguistic criteria
evaluation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 142 (1), 174–186.
Fiorenza, G., Sharma, V.K., Braccio, G., 2003. Techno-economic evaluation of a solar powered water desalination
plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 44 (14), 2217–2240.
Gude, V.G., Nirmalakhandan, N., Deng, S., 2010. Renewable and sustainable approaches for desalination. Renew.
Sust. Energ. Rev. 14 (9), 2641–2654.
Guo, S., Zhao, H., 2017. Fuzzy best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method and its applications. Knowl.-Based
Syst. 121, 23–31.