Page 159 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 159
Lignocellulosic biomass to biodiesel 133
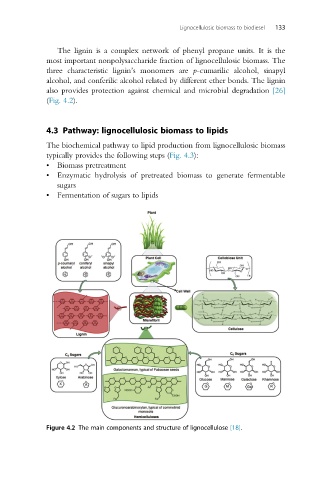
The lignin is a complex network of phenyl propane units. It is the
most important nonpolysaccharide fraction of lignocellulosic biomass. The
three characteristic lignin’s monomers are p-cumarilic alcohol, sinapyl
alcohol, and conferilic alcohol related by different ether bonds. The lignin
also provides protection against chemical and microbial degradation [26]
(Fig. 4.2).
4.3 Pathway: lignocellulosic biomass to lipids
The biochemical pathway to lipid production from lignocellulosic biomass
typically provides the following steps (Fig. 4.3):
• Biomass pretreatment
• Enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated biomass to generate fermentable
sugars
• Fermentation of sugars to lipids
Figure 4.2 The main components and structure of lignocellulose [18].