Page 164 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 164
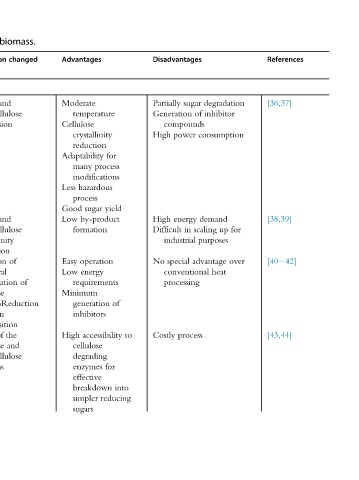
References [36,37] [38,39] [40 42] [43,44]
degradation inhibitor consumption demand for up scaling purposes over advantage heat
Disadvantages sugar Partially of Generation compounds power High energy High in Difficult industrial special No conventional processing process Costly
to for into reducing
yield
process
of
for
Advantages Moderate temperature Cellulose crystallinity reduction Adaptability many modifications hazardous Less process sugar Good by-product Low formation operation Easy energy Low requirements Minimum generation inhibitors accessibility High cellulose degrading enzymes effective breakdown simpler
biomass. changed of of fractionReduction the and
of Composition and Cellulose hemicellulose conversion and Cellulose hemicellulose crystallinity disruption Degradation structural organization cellulose lignin in composition of Rupture cellulose hemicellulose fractions
pretreatment
the under H 3 PO 4
for grinding, process mixing,
used Procedure Chipping, milling Heating shear T . 300°C 1% 5%NaOH, 4 30 min 300 600 W Sonication 10 100 kHz
processes 50°C
various corn straw, wheat cane sweet sorghum bagasse stover, switchgrass, soybean stover, sugarcane rape bagasse, Miscanthus corn bagasse, switchgrass, Sorghum,
of Feedstock Rice stover, straw, and Corn Switchgrass, corn straw, Sugarcane stover, poplar
Summary size
4.2 reduction extrusion
Table Pretreatment process Physical Mechanical Mechanical Microwave Ultrasound