Page 168 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 168
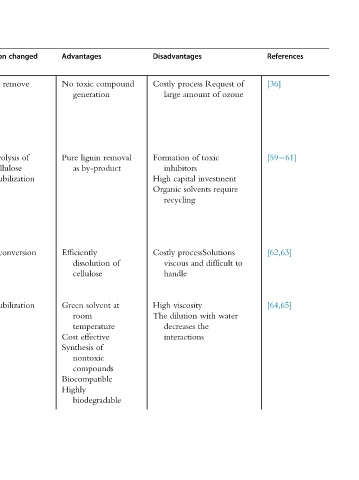
References [36] [59 61] [62,63] [64,65]
of ozone to
Request of toxic investment require processSolutions difficult water with the
Disadvantages process Costly amount large of Formation inhibitors capital High solvents Organic recycling Costly and viscous handle viscosity High dilution The decreases interactions
compound removal by-product of at solvent of
Advantages toxic No generation lignin Pure as Efficiently dissolution cellulose Green room temperature effective Cost Synthesis nontoxic compounds Biocompatible Highly biodegradable
changed remove of solubilization conversion solubilization
Composition Effectively lignin hydrolysis Total hemicellulose Lignin Cellulose Lignin
or min,
and ethanol, ethylene triethylene mixture H 2 SO 4 30 60 20:1 to 30 min sugars, and organic
room temperature, solvents (methanol, or of 1% pH 5 2.0 3.4 liquid/biomass equal urea, acids, other
Procedure Ozone, pressure Organic acetone, glycol, glycol) with HCl T 5 185°C, Ionic ratio T 5 120°C, Choline, amino several acids
straw, hay, straw, sugarcane pine straw, and stover straw
Feedstock Wheat bagasse, peanut, poplar, sawdust, green pine Wheat bagasse, poplar, spruce, Wheat bagasse, peanut, poplar corn Rice
(Continued)
4.2 liquids deep eutectic solvents
Table Pretreatment process Ozonolysis Organosolv Ionic Natural