Page 166 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 166
[45,46] [47,48] [36,49 56] [36,49,50,57,58] (Continued)
can pH salts of
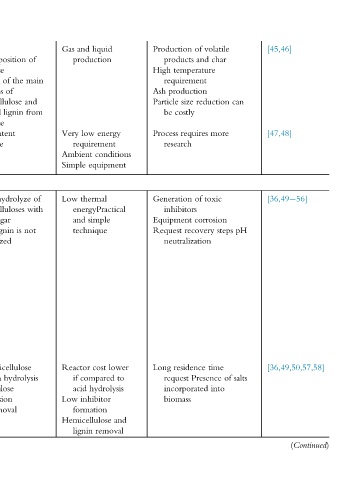
volatile char reduction more toxic corrosion steps time into
of and temperature requirement production size requires of recovery neutralization residence Presence incorporated
Production products High Ash Particle costly be Process research Generation inhibitors Equipment Request Long request biomass
liquid energy requirement conditions equipment thermal energyPractical simple lower cost to compared hydrolysis inhibitor and removal
and production low Ambient and technique Reactor if acid formation Hemicellulose lignin
Gas Very Simple Low Low
main from of with
of the and not is hydrolysis
decomposition of of hemicellulose lignin content hydrolyze hemicelluloses sugar yieldLignin solubilized hemicellulose cellulose conversion removal
Thermal cellulose Separation portions residual cellulose Lignin decrease Effective high High fraction High Lignin
cooling kV/ duration milliseconds) H 2 SO 4 ,HCl, for (5% high ratio 60°C, 4 h 35° v/v),
then condensing (5 20 short to process loads solids substrate/ for (10% 40% substrate/mixture) H 2 SO 4 Solid/Liquid NaOH, 120°C, H 2 O 2
T . 300°C, and voltage High for cm) (nano (Dilute) 0.75% 5% HNO 3 T 5 160°C 200°C P 5 1 MPa Continuous low 10% mixture) process Batch loads (Concentrated) 10% 30% T 5 170°C 190°C 1:2 Dilute h 24 Ca(OH) 2 , of Adding (0.5 2.15% C
waste corn switchgrass chip, switchgrass wood corn bagasse, wheat rye rice switchgrass corn bagasse, cane
Wood, cotton, stover, Wood Poplar stover, straw, straw, hulls, Hardwood, stover, leaves
electric hydrolysis hydrolysis
Pyrolysis Pulsed field Chemical Acid Alkaline