Page 172 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 172
References [36,76] [77,78] [36,79]
hydrogen and in processes
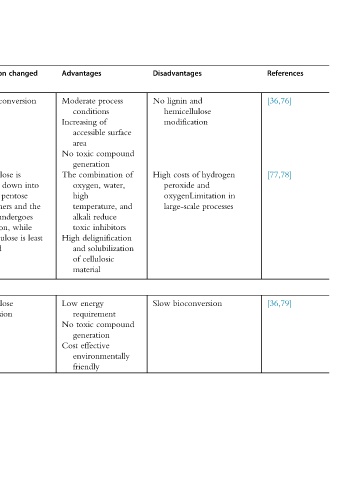
Disadvantages and lignin No hemicellulose modification of costs High peroxide oxygenLimitation large-scale bioconversion Slow
process of surface compound of combination water, and reduce inhibitors delignification solubilization cellulosic compound environmentally
Advantages Moderate conditions Increasing accessible area toxic No generation The oxygen, high temperature, alkali toxic High and of material energy Low requirement toxic No generation effective Cost friendly
changed conversion is into down pentose the and undergoes while least is
Composition Cellulose Hemicellulose broken smaller monomers lignin oxidation, cellulose the affected Hemicellulose conversion
with (120° 30 min) solid of
fiber along hydrogen high at hemicellulase degrading production using fermentation
Procedure CO 2 /kg 4kg P 5 5.6 MPa Air/oxygen or water peroxide temperature C 170°C, Cellulase, lignin and enzyme fungi by state biomass
straw, sugarcane reed, husk straw, straw, stover
Feedstock Wheat bagasse, recycled paper Common rice Wheat rice corn
(Continued) AFEX, Ammonia fiber explosion; LHW, liquid hot water.
4.2 explosion oxidation
Table Pretreatment process CO 2 Wet Biological Biological