Page 75 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 75
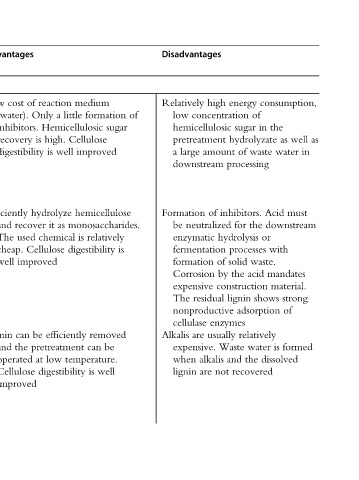
consumption, the as well as in water must Acid downstream or with mandates material. strong shows of formed is dissolved
energy of concentration in sugar hydrolyzate waste of amount processing inhibitors. the for hydrolysis processes waste. solid of acid the by construction lignin adsorption enzymes relatively usually water Waste the and recovered not
Disadvantages high Relatively low hemicellulosic pretreatment large a downstream of Formation neutralized be enzymatic fermentation formation Corrosion expensive residual The nonproductive cellulase are Alkalis expensive. alkalis when are lignin
of sugar is
medium formation little Cellulose improved hemicellulose monosaccharides. relatively is digestibility removed be can temperature. well is
reaction a Only Hemicellulosic high. is well is hydrolyze as it chemical Cellulose improved efficiently be pretreatment low at digestibility
Advantages of cost Low (water). inhibitors. recovery digestibility Efficiently recover and used The cheap. well can Lignin the and operated Cellulose improved
high high partial wall surface
to pretreat and biomass. at hemicelluloses cellulose lignin biomass porosity linkages and Cell with and
mechanisms digestibility to temperature external any pretreat acid acidic a hydrolyze and hydrolyze modify reduce increase lignin the the carbohydrate delignification deconstructed porosity
and water hot high without to added an as to of part lignin the to acid and as well and digest break and lignin hemicelluloses. is in
action cellulose liquid at plays disrupt mineral hemicelluloses as size to alkalis and in of thus increase
of biomass pressure chemicals Water temperature considerable structures structure particle structure between resulting removal structure great area.
Mode improve Using and Using Using
(Continued) pretreatment water
2.2 Pretreatment hot (hydrothermal) pretreatment acid prehydrolysis pretreatment
Table methods Chemical Liquid Dilute Alkaline