Page 200 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 200
AN INTRODUCTION TO PRIMARY BATTERIES 8.13
3.0
Li/MnO 2
2.0
Zn/Ag O
2
Voltage, V Zn/air
1.0
Zn/HgO
Alkaline-MnO 2
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 600
Discharge capacity, mAh
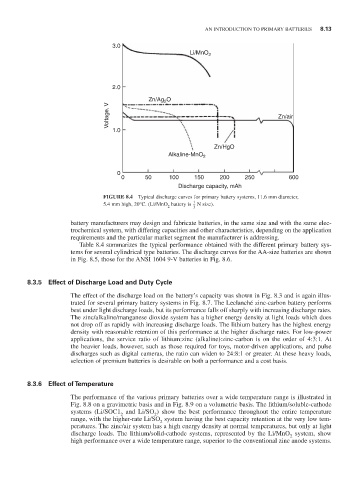
FIGURE 8.4 Typical discharge curves for primary battery systems, 11.6 mm diameter,
1
5.4 mm high, 20°C. (Li/MnO battery is N size).
3
2
battery manufacturers may design and fabricate batteries, in the same size and with the same elec-
trochemical system, with differing capacities and other characteristics, depending on the application
requirements and the particular market segment the manufacturer is addressing.
Table 8.4 summarizes the typical performance obtained with the different primary battery sys-
tems for several cylindrical type batteries. The discharge curves for the AA-size batteries are shown
in Fig. 8.5, those for the ANSI 1604 9-V batteries in Fig. 8.6.
8.3.5 Effect of Discharge Load and Duty Cycle
The effect of the discharge load on the battery’s capacity was shown in Fig. 8.3 and is again illus-
trated for several primary battery systems in Fig. 8.7. The Leclanché zinc-carbon battery performs
best under light discharge loads, but its performance falls off sharply with increasing discharge rates.
The zinc/alkaline/manganese dioxide system has a higher energy density at light loads which does
not drop off as rapidly with increasing discharge loads. The lithium battery has the highest energy
density with reasonable retention of this performance at the higher discharge rates. For low-power
applications, the service ratio of lithium:zinc (alkaline):zinc-carbon is on the order of 4:3:1. At
the heavier loads, however, such as those required for toys, motor-driven applications, and pulse
discharges such as digital cameras, the ratio can widen to 24:8:1 or greater. At these heavy loads,
selection of premium batteries is desirable on both a performance and a cost basis.
8.3.6 Effect of Temperature
The performance of the various primary batteries over a wide temperature range is illustrated in
Fig. 8.8 on a gravimetric basis and in Fig. 8.9 on a volumetric basis. The lithium/soluble-cathode
systems (Li/SOC1 and Li/SO ) show the best performance throughout the entire temperature
2
2
range, with the higher-rate Li/SO system having the best capacity retention at the very low tem-
2
peratures. The zinc/air system has a high energy density at normal temperatures, but only at light
discharge loads. The lithium/solid-cathode systems, represented by the Li/MnO system, show
2
high performance over a wide temperature range, superior to the conventional zinc anode systems.