Page 359 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 359
14.24 PriMAry BATTerieS
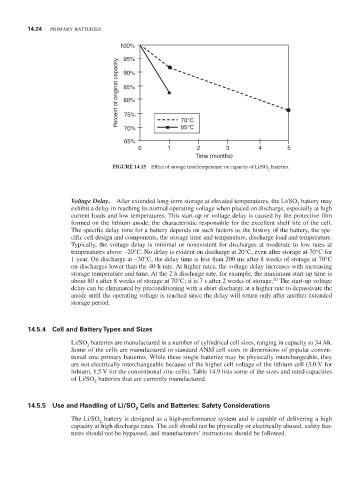
100%
95%
Percent of original capacity 90%
85%
80%
75%
85°C
70%
65% 70°C
0 1 2 3 4 5
Time (months)
FIGURE 14.15 effect of storage time/temperature on capacity of Li/SO batteries.
2
Voltage Delay. After extended long-term storage at elevated temperatures, the Li/SO battery may
2
exhibit a delay in reaching its normal operating voltage when placed on discharge, especially at high
current loads and low temperatures. This start-up or voltage delay is caused by the protective film
formed on the lithium anode, the characteristic responsible for the excellent shelf life of the cell.
The specific delay time for a battery depends on such factors as the history of the battery, the spe-
cific cell design and components, the storage time and temperature, discharge load and temperature.
Typically, the voltage delay is minimal or nonexistent for discharges at moderate to low rates at
temperatures above -20°C. No delay is evident on discharge at 20°C, even after storage at 70°C for
1 year. On discharge at -30°C, the delay time is less than 200 ms after 8 weeks of storage at 70°C
on discharges lower than the 40 h rate. At higher rates, the voltage delay increases with increasing
storage temperature and time. At the 2 h discharge rate, for example, the maximum start-up time is
20
about 80 s after 8 weeks of storage at 70°C; it is 7 s after 2 weeks of storage. The start-up voltage
delay can be eliminated by preconditioning with a short discharge at a higher rate to depassivate the
anode until the operating voltage is reached since the delay will return only after another extended
storage period.
14.5.4 Cell and Battery Types and Sizes
Li/SO batteries are manufactured in a number of cylindrical cell sizes, ranging in capacity to 34 Ah.
2
Some of the cells are manufactured in standard ANSi cell sizes in dimensions of popular conven-
tional zinc primary batteries. While these single batteries may be physically interchangeable, they
are not electrically interchangeable because of the higher cell voltage of the lithium cell (3.0 V for
lithium, 1.5 V for the conventional zinc cells). Table 14.9 lists some of the sizes and rated capacities
of Li/SO batteries that are currently manufactured.
2
14.5.5 Use and Handling of Li/SO Cells and Batteries: Safety Considerations
2
The Li/SO battery is designed as a high-performance system and is capable of delivering a high
2
capacity at high discharge rates. The cell should not be physically or electrically abused, safety fea-
tures should not be bypassed, and manufacturers’ instructions should be followed.