Page 18 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 18
MATLAB Basics ——— 3
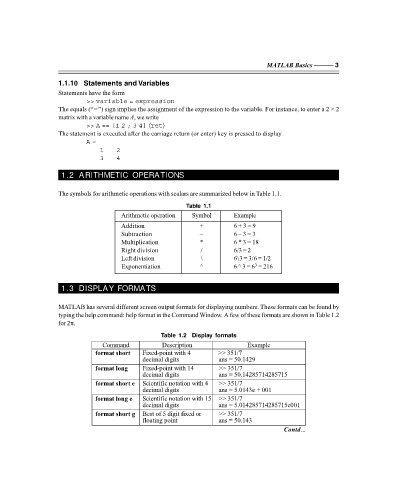
1.1.10 Statements and Variables
Statements have the form
>> variable = expression
The equals (“=”) sign implies the assignment of the expression to the variable. For instance, to enter a 2 × 2
matrix with a variable name A, we write
>> A == [1 2 ; 3 4] 〈ret〉
The statement is executed after the carriage return (or enter) key is pressed to display
A =
1 2
3 4
1.2 ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
The symbols for arithmetic operations with scalars are summarized below in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1
Arithmetic operation Symbol Example
Addition + 6 + 3 = 9
Subtraction – 6 – 3 = 3
Multiplication * 6 * 3 = 18
Right division / 6/3 = 2
Left division \ 6\3 = 3/6 = 1/2
3
Exponentiation ^ 6 ^ 3 = 6 = 216
1.3 DISPLAY FORMATS
MATLAB has several different screen output formats for displaying numbers. These formats can be found by
typing the help command: help format in the Command Window. A few of these formats are shown in Table 1.2
for 2π.
Table 1.2 Display formats
Command Description Example
format short Fixed-point with 4 >> 351/7
decimal digits ans = 50.1429
format long Fixed-point with 14 >> 351/7
decimal digits ans = 50.14285714285715
format short e Scientific notation with 4 >> 351/7
decimal digits ans = 5.0143e + 001
format long e Scientific notation with 15 >> 351/7
decimal digits ans = 5.014285714285715e001
format short g Best of 5 digit fixed or >> 351/7
floating point ans = 50.143
Contd...
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09