Page 19 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 19
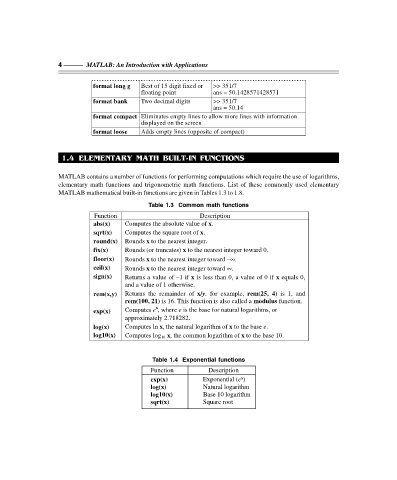
4 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
format long g Best of 15 digit fixed or >> 351/7
floating point ans = 50.1428571428571
format bank Two decimal digits >> 351/7
ans = 50.14
format compact Eliminates empty lines to allow more lines with information
displayed on the screen
format loose Adds empty lines (opposite of compact)
1.4 ELEMENTARY MATH BUILT-IN FUNCTIONS
MATLAB contains a number of functions for performing computations which require the use of logarithms,
elementary math functions and trigonometric math functions. List of these commonly used elementary
MATLAB mathematical built-in functions are given in Tables 1.3 to 1.8.
Table 1.3 Common math functions
Function Description
abs(x) Computes the absolute value of x.
sqrt(x) Computes the square root of x.
round(x) Rounds x to the nearest integer.
fix(x) Rounds (or truncates) x to the nearest integer toward 0.
floor(x) Rounds x to the nearest integer toward –∞.
ceil(x) Rounds x to the nearest integer toward ∞.
sign(x) Returns a value of –1 if x is less than 0, a value of 0 if x equals 0,
and a value of 1 otherwise.
rem(x,y) Returns the remainder of x/y. for example, rem(25, 4) is 1, and
rem(100, 21) is 16. This function is also called a modulus function.
x
exp(x) Computes e , where e is the base for natural logarithms, or
approximately 2.718282.
log(x) Computes ln x, the natural logarithm of x to the base e.
log10(x) Computes log 10 x, the common logarithm of x to the base 10.
Table 1.4 Exponential functions
Function Description
x
exp(x) Exponential (e )
log(x) Natural logarithm
log10(x) Base 10 logarithm
sqrt(x) Square root
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09