Page 20 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 20
MATLAB Basics ——— 5
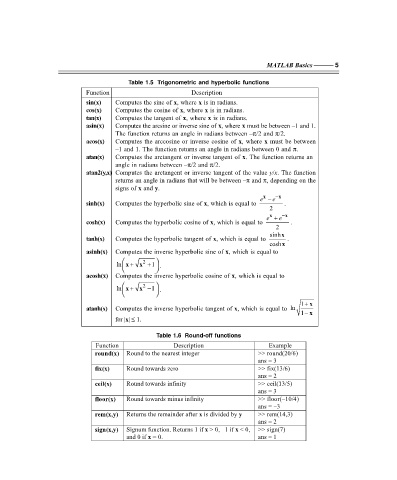
Table 1.5 Trigonometric and hyperbolic functions
Function Description
sin(x) Computes the sine of x, where x is in radians.
cos(x) Computes the cosine of x, where x is in radians.
tan(x) Computes the tangent of x, where x is in radians.
asin(x) Computes the arcsine or inverse sine of x, where x must be between –1 and 1.
The function returns an angle in radians between –π/2 and π/2.
acos(x) Computes the arccosine or inverse cosine of x, where x must be between
–1 and 1. The function returns an angle in radians between 0 and π.
atan(x) Computes the arctangent or inverse tangent of x. The function returns an
angle in radians between –π/2 and π/2.
atan2(y,x) Computes the arctangent or inverse tangent of the value y/x. The function
returns an angle in radians that will be between –π and π, depending on the
signs of x and y.
x
e − e −x
sinh(x) Computes the hyperbolic sine of x, which is equal to .
2
x
e + e −x
cosh(x) Computes the hyperbolic cosine of x, which is equal to .
2
sinhx
tanh(x) Computes the hyperbolic tangent of x, which is equal to .
coshx
asinh(x) Computes the inverse hyperbolic sine of x, which is equal to
2
ln x + x + 1 .
acosh(x) Computes the inverse hyperbolic cosine of x, which is equal to
2
ln x + x − 1 .
1+ x
atanh(x) Computes the inverse hyperbolic tangent of x, which is equal to ln
1− x
for |x| ≤ 1.
Table 1.6 Round-off functions
Function Description Example
round(x) Round to the nearest integer >> round(20/6)
ans = 3
fix( )x Round towards zero >> fix(13/6)
ans = 2
ceil( )x Round towards infinity >> ceil(13/5)
ans = 3
floor( )x Round towards minus infinity >> floor(–10/4)
ans = –3
rem(x,y) Returns the remainder after x is divided by y >> rem(14,3)
ans = 2
sign(x,y) Signum function. Returns 1 if x > 0, –1 if x < 0, >> sign(7)
and 0 if x = 0. ans = 1
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09