Page 54 - MATLAB Recipes for Earth Sciences
P. 54
3.4 Theoretical Distributions 45
Probability Density Probability Density
Function λ=0.5 Function λ=2
0.8 0.8
0.7 0.7
0.6 0.6
0.5 0.5
f(x) 0.4 f(x) 0.4
0.3 0.3
0.2 0.2
0.1 0.1
0 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
x x
a b
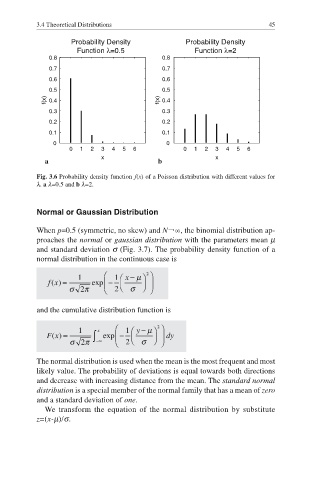
Fig. 3.6 Probability density function f(x) of a Poisson distribution with different values for
λ. a λ=0.5 and b λ=2.
Normal or Gaussian Distribution
When p=0.5 (symmetric, no skew) and N|, the binomial distribution ap-
proaches the normal or gaussian distribution with the parameters mean µ
and standard deviation σ (Fig. 3.7). The probability density function of a
normal distribution in the continuous case is
and the cumulative distribution function is
The normal distribution is used when the mean is the most frequent and most
likely value. The probability of deviations is equal towards both directions
and decrease with increasing distance from the mean. The standard normal
distribution is a special member of the normal family that has a mean of zero
and a standard deviation of one.
We transform the equation of the normal distribution by substitute
z=(x-µ)/σ.