Page 89 -
P. 89
3-44 MEMS: Design and Fabrication
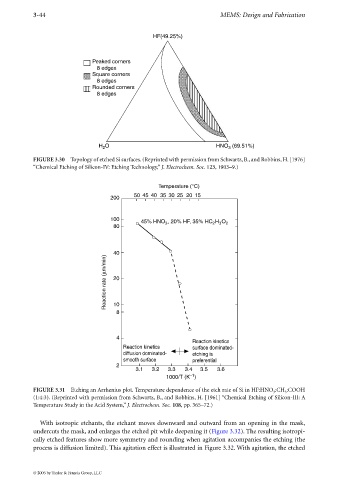
HF(49.25%)
Peaked corners
8 edges
Square corners
8 edges
Rounded corners
8 edges
H O HNO (69.51%)
3
2
FIGURE 3.30 Topology of etched Si surfaces. (Reprinted with permission from Schwartz, B., and Robbins, H. [1976]
“Chemical Etching of Silicon-IV: Etching Technology,” J. Electrochem. Soc. 123, 1903–9.)
Temperature (°C)
50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15
200
100 45% HNO , 20% HF, 35% HC H O 2
3
2
3
80
40
Reaction rate (µm/min) 20
10
8
4
Reaction kinetics
Reaction kinetics surface dominated-
diffusion dominated- etching is
smooth surface preferential
2
3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6
–1
1000/T (K )
FIGURE 3.31 Etching an Arrhenius plot. Temperature dependence of the etch rate of Si in HF:HNO :CH :COOH
3
3
(1:4:3). (Reprinted with permission from Schwartz, B., and Robbins, H. [1961] “Chemical Etching of Silicon-III: A
Temperature Study in the Acid System,” J. Electrochem. Soc. 108, pp. 365–72.)
With isotropic etchants, the etchant moves downward and outward from an opening in the mask,
undercuts the mask, and enlarges the etched pit while deepening it (Figure 3.32). The resulting isotropi-
cally etched features show more symmetry and rounding when agitation accompanies the etching (the
process is diffusion limited). This agitation effect is illustrated in Figure 3.32. With agitation, the etched
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC