Page 17 - Machinery Component Maintenance
P. 17
4 Machinery Component Maintenance and Repair
It is the awareness that true cost savings and profitability can only be
achieved by combining machinery reliability, safety, availability, and
maintainability into a cost-effective total-consistent with the intent of
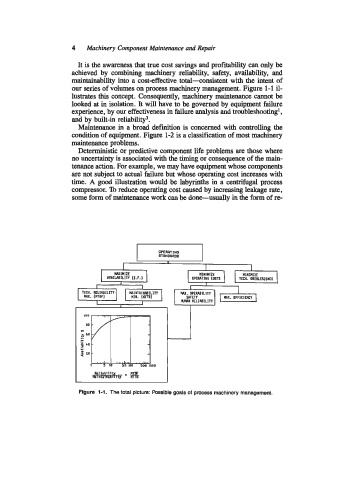
our series of volumes on process machinery management. Figure 1-1 il-
lustrates this concept. Consequently, machinery maintenance cannot be
looked at in isolation. It will have to be governed by equipment failure
experience, by our effectiveness in failure analysis and troubleshooting',
and by built-in reliability3.
Maintenance in a broad definition is concerned with controlling the
condition of equipment. Figure 1-2 is a classification of most machinery
maintenance problems.
Deterministic or predictive component life problems are those where
no uncertainty is associated with the timing or consequence of the main-
tenance action. For example, we may have equipment whose components
are not subject to actual failure but whose operating cost increases with
time. A good illustration would be labyrinths in a centrifugal process
compressor. To reduce operating cost caused by increasing leakage rate,
some form of maintenance work can be done-usually in the form of re
I OPERRTINB I
STFINDQRDS
AVAILABILITY (S.F.) OPERATING COSTS TECH. OBSOLESCENCE
Eux. (MTBF) MlN. (KITR) RX. EFFICIENCY
Figure 1-1. The total picture: Possible goals of process machinery management.