Page 204 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 204
ELECTRON DENSITY FITTING AND STRUCTURE VALIDATION 193
outlier is highly suspect, even though the den- side-chain dihedral sensibility, agreement with the
sity fit is decent. For example, a valine side chain electron density map, and potential energy. The
may require ‘flipping’ by a 180 degree rotation. real-space R-factor (RSR) (Jones et al., 1991) is a
WHATCHECK (Hooft et al., 1996) (www.cmbi.kun. particularly powerful tool for detecting stretches of
nl/gv/whatcheck), the validation module of Gert residues that are out of register. The temperature fac-
Vriend’s molecular modelling program WHATIF tor, or B-factor, can be a sink for absorbing errors.
(Vriend, 1990), is preferred locally to carry out Any residues with values over 40 may be closer
conformational analyses. Its flagging of question- to fantasy than reality. In a study designed to find
able rotamers may not be as good as PROCHECK, errors in a molecular replacement model (Carson
but it offers many important additional checks. et al., 1994), RSR, B-factors, convergence of refine-
Stretches of residues are analysed for packing and ment, dihedral fit to the database, and geometric
via a database comparisons. This can identify strain were found to predict error. In perhaps a tau-
bad stretches that actually have reasonable dihe- tology, the most important factors were the RSR and
dral angles, or carbonyls that need to be flipped. B-factors. The contribution of the X-ray data is the
The hydrogen bonding pattern analysis reveals any most important – the structure cannot be judged by
unsatisfied main-chain hydrogen bonds, and Asn, geometry alone.
Gln, and His side chains that should be flipped. An The emerging field of structural genomics will
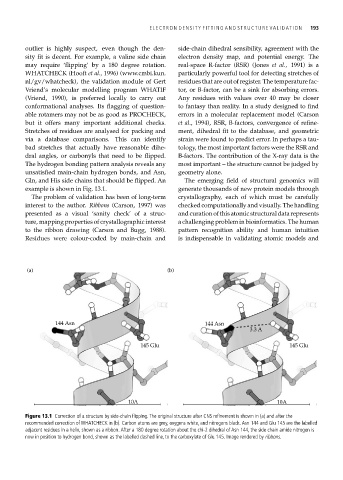
example is shown in Fig. 13.1. generate thousands of new protein models through
The problem of validation has been of long-term crystallography, each of which must be carefully
interest to the author. Ribbons (Carson, 1997) was checked computationally and visually. The handling
presented as a visual ‘sanity check’ of a struc- and curation of this atomic structural data represents
ture, mapping properties of crystallographic interest a challenging problem in bioinformatics. The human
to the ribbon drawing (Carson and Bugg, 1988). pattern recognition ability and human intuition
Residues were colour-coded by main-chain and is indispensable in validating atomic models and
(a) (b)
144 Asn 144 Asn
3.3 A
145 Glu 145 Glu
10A 10A
Figure 13.1 Correction of a structure by side-chain flipping. The original structure after CNS refinement is shown in (a) and after the
recommended correction of WHATCHECK in (b). Carbon atoms are grey, oxygens white, and nitrogens black. Asn 144 and Glu 145 are the labelled
adjacent residues in a helix, shown as a ribbon. After a 180 degree rotation about the chi-2 dihedral of Asn 144, the side chain amide nitrogen is
now in position to hydrogen bond, shown as the labelled dashed line, to the carboxylate of Glu 145. Image rendered by ribbons.