Page 43 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 43
32 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
Cleared or crude cell lysate expression of His-tagged proteins was monitored by
SDS-PAGE, in combination with western blotting,
following small-scale Ni-NTA purification using fil-
ter plates. Levels of expression of around 5 µg/ml
were reported and shown to be scaleable in shake
flask cultures. No obvious differences between
yields from the two yeasts were observed for the
Bind NTA-Ni 2+ same proteins even under controlled fermentation
conditions (Prinz et al., 2004).
2.3.2.2 Higher eukaryotic cells
Wash
Baculovirus infection of insect cells has been widely
‘Do you want to used, particularly in a pharmaceutical company set-
elute protein ting, for producing enzyme targets for inhibitor
from the beads?’
screening, notably kinases (Chambers et al., 2004).
‘Yes’ ‘No’
This has led to the development of microplate
formats for both baculovirus construction and sub-
NTA-Ni 2+ sequent expression screening. As with yeast sys-
tems, expression of His-tagged proteins is assayed
using anti-His antibodies by western blotting (Bahia
Pure 6xHis-tagged protein et al., 2005). Less attention has been paid to the
use of mammalian cells for HTP protein expression,
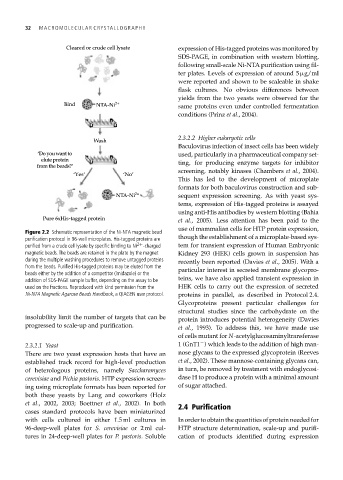
Figure 2.2 Schematic representation of the Ni-NTA magnetic bead
purification protocol in 96-well microplates. His-tagged proteins are though the establishment of a microplate-based sys-
purified from a crude cell lysate by specific binding to Ni 2+ -charged tem for transient expression of Human Embryonic
magnetic beads. The beads are retained in the plate by the magnet Kidney 293 (HEK) cells grown in suspension has
during the multiple washing procedures to remove untagged proteins recently been reported (Davies et al., 2005). With a
from the beads. Purified His-tagged proteins may be eluted from the particular interest in secreted membrane glycopro-
beads either by the addition of a competitor (imidazole) or the
addition of SDS-PAGE sample buffer, depending on the assay to be teins, we have also applied transient expression in
used on the fractions. Reproduced with kind permission from the HEK cells to carry out the expression of secreted
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads Handbook, a QIAGEN user protocol. proteins in parallel, as described in Protocol 2.4.
Glycoproteins present particular challenges for
structural studies since the carbohydrate on the
insolubility limit the number of targets that can be
protein introduces potential heterogeneity (Davies
progressed to scale-up and purification.
et al., 1993). To address this, we have made use
of cells mutant for N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
−
2.3.2.1 Yeast 1 (GnT1 ) which leads to the addition of high man-
There are two yeast expression hosts that have an nose glycans to the expressed glycoprotein (Reeves
established track record for high-level production et al., 2002). These mannose-containing glycans can,
of heterologous proteins, namely Saccharomyces in turn, be removed by treatment with endoglycosi-
cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris. HTP expression screen- dase H to produce a protein with a minimal amount
ing using microplate formats has been reported for of sugar attached.
both these yeasts by Lang and coworkers (Holz
et al., 2002, 2003; Boettner et al., 2002). In both
2.4 Purification
cases standard protocols have been miniaturized
with cells cultured in either 1.5 ml cultures in In order to obtain the quantities of protein needed for
96-deep-well plates for S. cerevisiae or 2 ml cul- HTP structure determination, scale-up and purifi-
tures in 24-deep-well plates for P. pastoris. Soluble cation of products identified during expression