Page 41 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 41
30 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
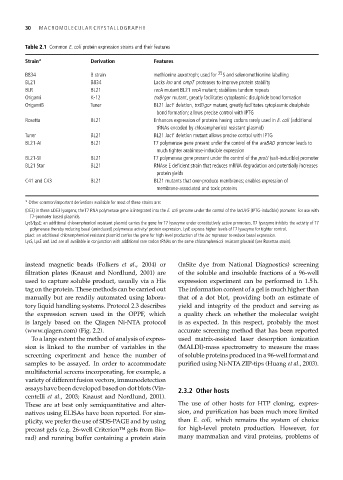
Table 2.1 Common E. coli protein expression strains and their features
Strain* Derivation Features
B834 B strain methionine auxotroph; used for 35 S and selenomethionine labelling
BL21 B834 Lacks lon and ompT proteases to improve protein stability
BLR BL21 recA mutant BL21 recA mutant; stabilizes tandem repeats
Origami K-12 trxB/gor mutant, greatly facilitates cytoplasmic disulphide bond formation
OrigamiB Tuner BL21 lacY deletion, trxB/gor mutant, greatly facilitates cytoplasmic disulphide
bond formation; allows precise control with IPTG
Rosetta BL21 Enhances expression of proteins having codons rarely used in E. coli (additional
tRNAs encoded by chloramphenicol resistant plasmid)
Tuner BL21 BL21 lacY deletion mutant allows precise control with IPTG
BL21-AI BL21 T7 polymerase gene present under the control of the araBAD promoter leads to
much tighter arabinose-inducible expression
BL21-SI BL21 T7 polymerase gene present under the control of the proU (salt-inducible) promoter
BL21 Star BL21 RNAse E deficient strain that reduces mRNA degradation and potentially increases
protein yields
C41 and C43 BL21 BL21 mutants that over-produce membranes; enables expression of
membrane-associated and toxic proteins
* Other common/important derivations available for most of these strains are:
(DE3) in these λDE3 lysogens, the T7 RNA polymerase gene is integrated into the E. coli genome under the control of the lacUV5 (IPTG-inducible) promoter. For use with
T7-promoter based plasmids.
LysS/LysE: an additional chloramphenicol resistant plasmid carries the gene for T7 lysozyme under constitutively active promoters. T7 lysozyme inhibits the activity of T7
polymerase thereby reducing basal (uninduced) polymerase activity/ protein expression. LysE express higher levels of T7 lysozyme for tighter control.
pLacI: an additional chloramphenicol resistant plasmid carries the gene for high level production of the lac repressor to reduce basal expression.
LysS, LysE and LacI are all available in conjunction with additional rare codon tRNAs on the same chloramphenicol resistant plasmid (see Rosettas strain).
instead magnetic beads (Folkers et al., 2004) or (InSite dye from National Diagnostics) screening
filtration plates (Knaust and Nordlund, 2001) are of the soluble and insoluble fractions of a 96-well
used to capture soluble product, usually via a His expression experiment can be performed in 1.5 h.
tag on the protein. These methods can be carried out The information content of a gel is much higher than
manually but are readily automated using labora- that of a dot blot, providing both an estimate of
tory liquid handling systems. Protocol 2.3 describes yield and integrity of the product and serving as
the expression screen used in the OPPF, which a quality check on whether the molecular weight
is largely based on the Qiagen Ni-NTA protocol is as expected. In this respect, probably the most
(www.qiagen.com) (Fig. 2.2). accurate screening method that has been reported
To a large extent the method of analysis of expres- used matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization
sion is linked to the number of variables in the (MALDI)-mass spectrometry to measure the mass
screening experiment and hence the number of of soluble proteins produced in a 96-well format and
samples to be assayed. In order to accommodate purified using Ni-NTA ZIP-tips (Huang et al., 2003).
multifactorial screens incorporating, for example, a
variety of different fusion vectors, immunodetection
assays have been developed based on dot blots (Vin- 2.3.2 Other hosts
centelli et al., 2003; Knaust and Nordlund, 2001).
These are at best only semiquantitative and alter- The use of other hosts for HTP cloning, expres-
natives using ELISAs have been reported. For sim- sion, and purification has been much more limited
plicity, we prefer the use of SDS-PAGE and by using than E. coli, which remains the system of choice
precast gels (e.g. 26-well Criterion™ gels from Bio- for high-level protein production. However, for
rad) and running buffer containing a protein stain many mammalian and viral proteins, problems of