Page 37 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 37
26 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
(c) In-Fusion TM (custom)
Entry Clone (attL Kan ) r pDEST ( att RAmp ) r
Linearize vector Purify ‘In-Fusion-
and purify tagged’ PCR product
LR Clonase reaction 1 Hour at
25˚C, Proteinase K ‘kill’ reaction at
37˚C for 10 min
Expression Clone (attB Amp ) r By-product Vector (ccdB Kan ) r
+
React with In-Fusion enzyme,
30 min at 42˚C Transform into E.coli , Normally
plated on 4 X 24-well LB Agar
Plates supplemented with Ampicillin
Transform into E.coli
8
(competency >10 c.f.u./µg DNA),
Plasmid ‘backbone’ repaired/ligated
by E.coli, Normally in 24-well plates Pick colonies, grow, prepare
plasmid, PCR screen for insert
Expression-ready
plasmid minipreps
Pick ‘whites’, grow, prepare
plasmid, PCR screen for insert
Expression-ready
plasmid minipreps
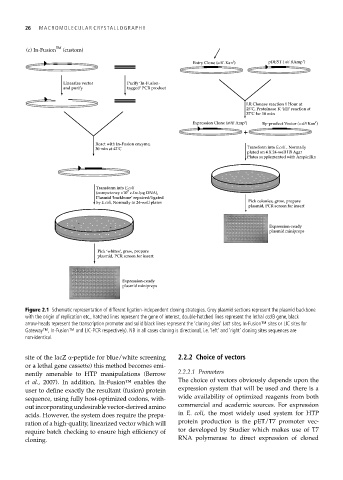
Figure 2.1 Schematic representation of different ligation-independent cloning strategies. Grey plasmid sections represent the plasmid backbone
with the origin of replication etc., hatched lines represent the gene of interest, double-hatched lines represent the lethal ccdB gene, black
arrow-heads represent the transcription promoter and solid black lines represent the ‘cloning sites’ (att sites, In-Fusion™ sites or LIC sites for
Gateway™, In-Fusion™ and LIC-PCR respectively). NB in all cases cloning is directional, i.e. ‘left’ and ‘right’ cloning sites sequences are
non-identical.
site of the lacZ α-peptide for blue/white screening 2.2.2 Choice of vectors
or a lethal gene cassette) this method becomes emi-
nently amenable to HTP manipulations (Berrow 2.2.2.1 Promoters
et al., 2007). In addition, In-Fusion™ enables the The choice of vectors obviously depends upon the
user to define exactly the resultant (fusion) protein expression system that will be used and there is a
sequence, using fully host-optimized codons, with- wide availability of optimized reagents from both
out incorporating undesirable vector-derived amino commercial and academic sources. For expression
acids. However, the system does require the prepa- in E. coli, the most widely used system for HTP
ration of a high-quality, linearized vector which will protein production is the pET/T7 promoter vec-
require batch checking to ensure high efficiency of tor developed by Studier which makes use of T7
cloning. RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned