Page 301 -
P. 301
300 Part Two Information Technology Infrastructure
Web Servers
A Web server is software for locating and managing stored Web pages. It locates
the Web pages requested by a user on the computer where they are stored and
delivers the Web pages to the user’s computer. Server applications usually run
on dedicated computers, although they can all reside on a single computer in
small organizations.
The most common Web server in use today is Apache HTTP Server, which
controls 65 percent of the market. Apache is an open source product that is free
of charge and can be downloaded from the Web. Microsoft Internet Information
Services (IIS) is the second most commonly used Web server, with 15 percent
market share.
Searching for Information on the Web
No one knows for sure how many Web pages there really are. The surface
Web is the part of the Web that search engines visit and about which informa-
tion is recorded. For instance, Google visited about 400 billion pages in 2012,
and this reflects a large portion of the publicly accessible Web page popula-
tion. But there is a “deep Web” that contains an estimated 1 trillion additional
pages, many of them proprietary (such as the pages of the Wall Street Journal
Online, which cannot be visited without a subscription or access code) or that
are stored in protected corporate databases.
Search Engines Obviously, with so many Web pages, finding specific Web
pages that can help you or your business, nearly instantly, is an important
problem. The question is, how can you find the one or two pages you really
want and need out of billions of indexed Web pages? Search engines attempt to
solve the problem of finding useful information on the Web nearly instantly,
and, arguably, they are the “killer app” of the Internet era. Today’s search
engines can sift through HTML files, files of Microsoft Office applications, PDF
files, as well as audio, video, and image files. There are hundreds of different
search engines in the world, but the vast majority of search results are supplied
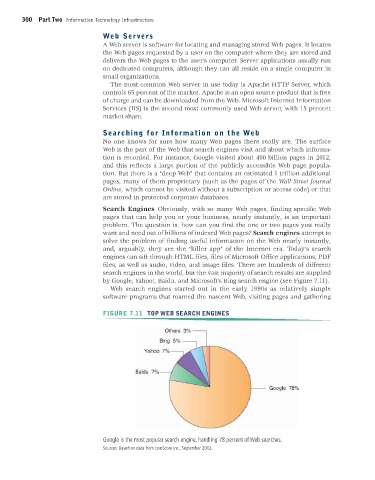
by Google, Yahoo!, Baidu, and Microsoft’s Bing search engine (see Figure 7.11).
Web search engines started out in the early 1990s as relatively simple
software programs that roamed the nascent Web, visiting pages and gathering
FIGURE 7.11 TOP WEB SEARCH ENGINES
Google is the most popular search engine, handling 78 percent of Web searches.
Sources: Based on data from comScore Inc., September 2012.
MIS_13_Ch_07_Global.indd 300 1/17/2013 2:28:32 PM