Page 302 -
P. 302
Chapter 7 Telecommunications, the Internet, and Wireless Technology 301
information about the content of each page. The first search engines were
simple keyword indexes of all the pages they visited, leaving the user with lists
of pages that may not have been truly relevant to their search.
In 1994, Stanford University computer science students David Filo and Jerry
Yang created a hand-selected list of their favorite Web pages and called it “Yet
Another Hierarchical Officious Oracle,” or Yahoo. Yahoo was not initially a search
engine but rather an edited selection of Web sites organized by categories the edi-
tors found useful, but currently relies on Microsoft for search results.
In 1998, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two other Stanford computer science
students, released their first version of Google. This search engine was different:
Not only did it index each Web page’s words but it also ranked search results
based on the relevance of each page. Page patented the idea of a page ranking
system (called PageRank System), which essentially measures the popularity of
a Web page by calculating the number of sites that link to that page as well as the
number of pages which it links to. The premise is that really popular Web pages
are more “relevant” to users. Brin contributed a unique Web crawler program that
indexed not only keywords on a page but also combinations of words (such as
authors and the titles of their articles). These two ideas became the foundation
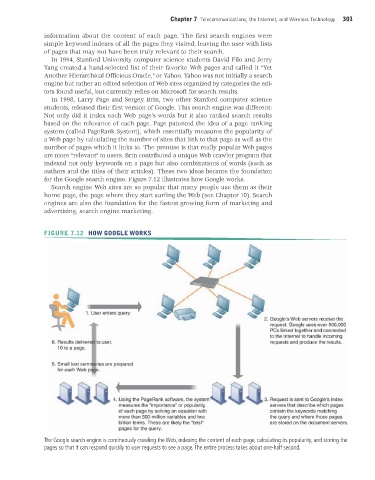
for the Google search engine. Figure 7.12 illustrates how Google works.
Search engine Web sites are so popular that many people use them as their
home page, the page where they start surfing the Web (see Chapter 10). Search
engines are also the foundation for the fastest growing form of marketing and
advertising, search engine marketing.
FIGURE 7.12 HOW GOOGLE WORKS
The Google search engine is continuously crawling the Web, indexing the content of each page, calculating its popularity, and storing the
pages so that it can respond quickly to user requests to see a page. The entire process takes about one-half second.
MIS_13_Ch_07_Global.indd 301 1/17/2013 2:28:32 PM