Page 326 -
P. 326
Chapter 8 Securing Information Systems 325
8.1 SYSTEM VULNERABILITY AND ABUSE
C an you imagine what would happen if you tried to link to the Internet
without a firewall or antivirus software? Your computer would be
disabled in a few seconds, and it might take you many days to recover.
If you used the computer to run your business, you might not be
able to sell to your customers or place orders with your suppliers while it was
down. And you might find that your computer system had been penetrated by
outsiders, who perhaps stole or destroyed valuable data, including confiden-
tial payment data from your customers. If too much data were destroyed or
divulged, your business might never be able to operate!
In short, if you operate a business today, you need to make security
and control a top priority. Security refers to the policies, procedures, and
technical measures used to prevent unauthorized access, alteration, theft,
or physical damage to information systems. Controls are methods, policies,
and organizational procedures that ensure the safety of the organization’s
assets, the accuracy and reliability of its records, and operational adherence to
management standards.
WHY SYSTEMS ARE VULNERABLE
When large amounts of data are stored in electronic form, they are vulnerable
to many more kinds of threats than when they existed in manual form. Through
communications networks, information systems in different locations are inter-
connected. The potential for unauthorized access, abuse, or fraud is not limited
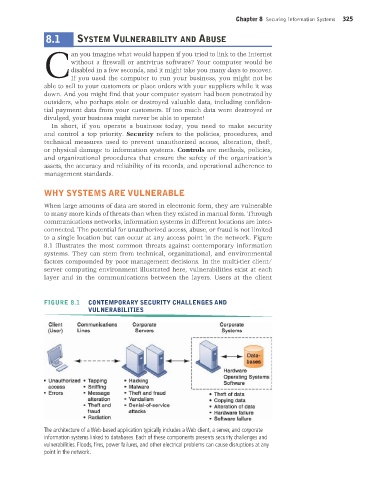
to a single location but can occur at any access point in the network. Figure
8.1 illustrates the most common threats against contemporary information
systems. They can stem from technical, organizational, and environmental
factors compounded by poor management decisions. In the multi-tier client/
server computing environment illustrated here, vulnerabilities exist at each
layer and in the communications between the layers. Users at the client
FIGURE 8.1 CONTEMPORARY SECURITY CHALLENGES AND
VULNERABILITIES
The architecture of a Web-based application typically includes a Web client, a server, and corporate
information systems linked to databases. Each of these components presents security challenges and
vulnerabilities. Floods, fires, power failures, and other electrical problems can cause disruptions at any
point in the network.
MIS_13_Ch_08 Global.indd 325 1/17/2013 3:10:19 PM