Page 325 -
P. 325
324 Part Two Information Technology Infrastructure
Immediately after the password theft, LinkedIn quickly assured its customers that
their data were secure. The company disabled the 6.5 million published passwords
and announced that it had begun an initiative to salt passwords to increase security.
Nevertheless, LinkedIn now faces a $5 million class-action lawsuit that asserts that
LinkedIn failed to follow even the minimal industry-standard practices for data
protection, specifically more recent forms of salting hashed passwords.
Security experts noted that LinkedIn’s security procedures would have been state
of the art several years ago, but that they had done little to keep up with and protect
themselves from the surge in data breaches in the last year or two. LinkedIn must
not only update their security to today’s standards, but must also adopt the mindset
that protecting consumer data is an ongoing effort, not a one-time fix.
Sources: LinkedIn Faces $5 Million Lawsuit After Password Breach,” CIO Insight, June 22, 2012;
“LinkedIn Defends Reaction in Wake of Password Theft,” The Wall Street Journal, June 10, 2012;
“Lax Security at LinkedIn Is Laid Bare,” The New York Times, June 10, 2012; “Why ID Thieves Love
Social Media,” Marketwatch, March 25, 2012.
he problems created by the theft of 6.5 million passwords at LinkedIn illustrate
Tsome of the reasons why businesses need to pay special attention to informa-
tion system security. LinkedIn provides important benefits to both individuals and
businesses. But from a security standpoint, LinkedIn did not sufficiently protect its
Web site from hackers, who were able to steal sensitive user information.
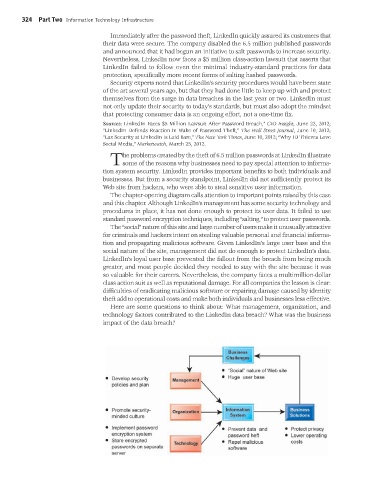
The chapter-opening diagram calls attention to important points raised by this case
and this chapter. Although LinkedIn’s management has some security technology and
procedures in place, it has not done enough to protect its user data. It failed to use
standard password encryption techniques, including “salting,” to protect user passwords.
The “social” nature of this site and large number of users make it unusually attractive
for criminals and hackers intent on stealing valuable personal and financial informa-
tion and propagating malicious software. Given LinkedIn’s large user base and the
social nature of the site, management did not do enough to protect LinkedIn’s data.
LinkedIn’s loyal user base prevented the fallout from the breach from being much
greater, and most people decided they needed to stay with the site because it was
so valuable for their careers. Nevertheless, the company faces a multimillion-dollar
class action suit as well as reputational damage. For all companies the lesson is clear:
difficulties of eradicating malicious software or repairing damage caused by identity
theft add to operational costs and make both individuals and businesses less effective.
Here are some questions to think about: What management, organization, and
technology factors contributed to the LinkedIn data breach? What was the business
impact of the data breach?
MIS_13_Ch_08 Global.indd 324 1/17/2013 3:10:19 PM