Page 411 -
P. 411
410 Part Three Key System Applications for the Digital Age
deal. Thus, the Web has reduced the information asymmetry surrounding an
auto purchase. The Internet has also helped businesses seeking to purchase
from other businesses reduce information asymmetries and locate better prices
and terms.
Digital markets are very flexible and efficient because they operate with
reduced search and transaction costs, lower menu costs (merchants’ costs of
changing prices), greater price discrimination, and the ability to change prices
dynamically based on market conditions. In dynamic pricing, the price of a
product varies depending on the demand characteristics of the customer or
the supply situation of the seller. For instance, online retailers from Amazon to
Walmart change prices on many products based on time of day, demand for the
product, and users’ prior visits to their sites.
These new digital markets may either reduce or increase switching costs,
depending on the nature of the product or service being sold, and they may
cause some extra delay in gratification. Unlike a physical market, you can’t
immediately consume a product such as clothing purchased over the Web
(although immediate consumption is possible with digital music downloads
and other digital products.)
Digital markets provide many opportunities to sell directly to the consumer,
bypassing intermediaries, such as distributors or retail outlets. Eliminating inter-
mediaries in the distribution channel can significantly lower purchase transac-
tion costs. To pay for all the steps in a traditional distribution channel, a product
may have to be priced as high as 135 percent of its original cost to manufacture.
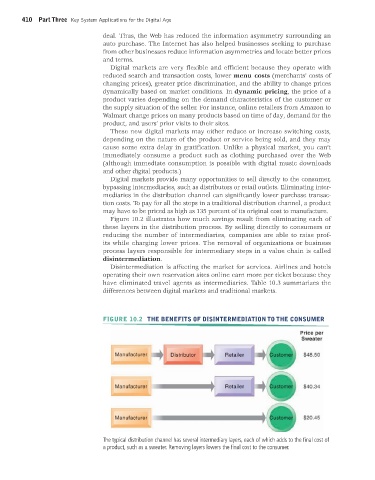
Figure 10.2 illustrates how much savings result from eliminating each of
these layers in the distribution process. By selling directly to consumers or
reducing the number of intermediaries, companies are able to raise prof-
its while charging lower prices. The removal of organizations or business
process layers responsible for intermediary steps in a value chain is called
disintermediation.
Disintermediation is affecting the market for services. Airlines and hotels
operating their own reservation sites online earn more per ticket because they
have eliminated travel agents as intermediaries. Table 10.3 summarizes the
differences between digital markets and traditional markets.
FIGURE 10.2 THE BENEFITS OF DISINTERMEDIATION TO THE CONSUMER
The typical distribution channel has several intermediary layers, each of which adds to the final cost of
a product, such as a sweater. Removing layers lowers the final cost to the consumer.
MIS_13_Ch_10 Global.indd 410 1/17/2013 2:29:35 PM