Page 431 -
P. 431
430 Part Three Key System Applications for the Digital Age
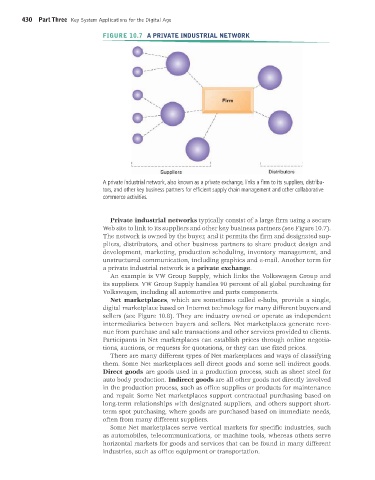
FIGURE 10.7 A PRIVATE INDUSTRIAL NETWORK
A private industrial network, also known as a private exchange, links a firm to its suppliers, distribu-
tors, and other key business partners for efficient supply chain management and other collaborative
commerce activities.
Private industrial networks typically consist of a large firm using a secure
Web site to link to its suppliers and other key business partners (see Figure 10.7).
The network is owned by the buyer, and it permits the firm and designated sup-
pliers, distributors, and other business partners to share product design and
development, marketing, production scheduling, inventory management, and
unstructured communication, including graphics and e-mail. Another term for
a private industrial network is a private exchange.
An example is VW Group Supply, which links the Volkswagen Group and
its suppliers. VW Group Supply handles 90 percent of all global purchasing for
Volkswagen, including all automotive and parts components.
Net marketplaces, which are sometimes called e-hubs, provide a single,
digital marketplace based on Internet technology for many different buyers and
sellers (see Figure 10.8). They are industry owned or operate as independent
intermediaries between buyers and sellers. Net marketplaces generate reve-
nue from purchase and sale transactions and other services provided to clients.
Participants in Net marketplaces can establish prices through online negotia-
tions, auctions, or requests for quotations, or they can use fixed prices.
There are many different types of Net marketplaces and ways of classifying
them. Some Net marketplaces sell direct goods and some sell indirect goods.
Direct goods are goods used in a production process, such as sheet steel for
auto body production. Indirect goods are all other goods not directly involved
in the production process, such as office supplies or products for maintenance
and repair. Some Net marketplaces support contractual purchasing based on
long-term relationships with designated suppliers, and others support short-
term spot purchasing, where goods are purchased based on immediate needs,
often from many different suppliers.
Some Net marketplaces serve vertical markets for specific industries, such
as automobiles, telecommunications, or machine tools, whereas others serve
horizontal markets for goods and services that can be found in many different
industries, such as office equipment or transportation.
MIS_13_Ch_10 Global.indd 430 1/17/2013 2:29:37 PM