Page 467 -
P. 467
466 Part Three Key System Applications for the Digital Age
Some expert systems, especially large ones, are so complex that in a few years
the maintenance costs equal the development costs.
ORGANIZATIONAL INTELLIGENCE: CASE-BASED
REASONING
Expert systems primarily capture the tacit knowledge of individual experts, but
organizations also have collective knowledge and expertise that they have built
up over the years. This organizational knowledge can be captured and stored
using case-based reasoning. In case-based reasoning (CBR), descriptions of
past experiences of human specialists, represented as cases, are stored in a
database for later retrieval when the user encounters a new case with similar
parameters. The system searches for stored cases with problem characteristics
similar to the new one, finds the closest fit, and applies the solutions of the old
case to the new case. Successful solutions are tagged to the new case and both
are stored together with the other cases in the knowledge base. Unsuccessful
solutions also are appended to the case database along with explanations as to
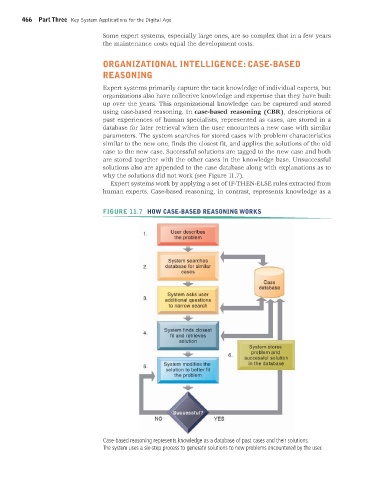
why the solutions did not work (see Figure 11.7).
Expert systems work by applying a set of IF-THEN-ELSE rules extracted from
human experts. Case-based reasoning, in contrast, represents knowledge as a
FIGURE 11.7 HOW CASE-BASED REASONING WORKS
Case-based reasoning represents knowledge as a database of past cases and their solutions.
The system uses a six-step process to generate solutions to new problems encountered by the user.
MIS_13_Ch_11 Global.indd 466 1/17/2013 2:30:05 PM