Page 249 - Managing Global Warming
P. 249
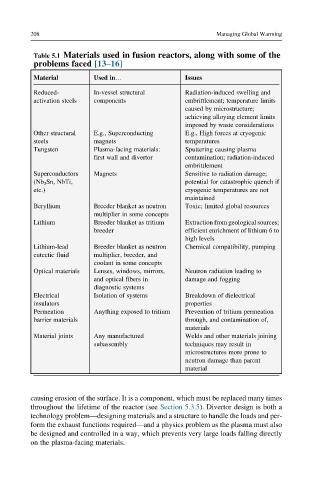
208 Managing Global Warming
Table 5.1 Materials used in fusion reactors, along with some of the
problems faced [13–16]
Used in…
Material Issues
Reduced- In-vessel structural Radiation-induced swelling and
activation steels components embrittlement; temperature limits
caused by microstructure;
achieving alloying element limits
imposed by waste considerations
Other structural E.g., Superconducting E.g., High forces at cryogenic
steels magnets temperatures
Tungsten Plasma-facing materials: Sputtering causing plasma
first wall and divertor contamination; radiation-induced
embrittlement
Superconductors Magnets Sensitive to radiation damage;
(Nb 3 Sn, NbTi, potential for catastrophic quench if
etc.) cryogenic temperatures are not
maintained
Beryllium Breeder blanket as neutron Toxic; limited global resources
multiplier in some concepts
Lithium Breeder blanket as tritium Extraction from geological sources;
breeder efficient enrichment of lithium 6 to
high levels
Lithium-lead Breeder blanket as neutron Chemical compatibility, pumping
eutectic fluid multiplier, breeder, and
coolant in some concepts
Optical materials Lenses, windows, mirrors, Neutron radiation leading to
and optical fibers in damage and fogging
diagnostic systems
Electrical Isolation of systems Breakdown of dielectrical
insulators properties
Permeation Anything exposed to tritium Prevention of tritium permeation
barrier materials through, and contamination of,
materials
Material joints Any manufactured Welds and other materials joining
subassembly techniques may result in
microstructures more prone to
neutron damage than parent
material
causing erosion of the surface. It is a component, which must be replaced many times
throughout the lifetime of the reactor (see Section 5.3.5). Divertor design is both a
technology problem—designing materials and a structure to handle the loads and per-
form the exhaust functions required—and a physics problem as the plasma must also
be designed and controlled in a way, which prevents very large loads falling directly
on the plasma-facing materials.