Page 251 - Managing Global Warming
P. 251
210 Managing Global Warming
The placement of magnetic coils and the sizes of components mean that access to
the reactor interior is difficult and the kinematics of component replacement compli-
cated. However, the economics of energy production depend on high availability and
this means that efficient maintenance systems must be designed. Basic designs for
such systems vary considerably between power plant concepts, but most involve some
sort of horizontal or vertical access port through which large sections of the blanket
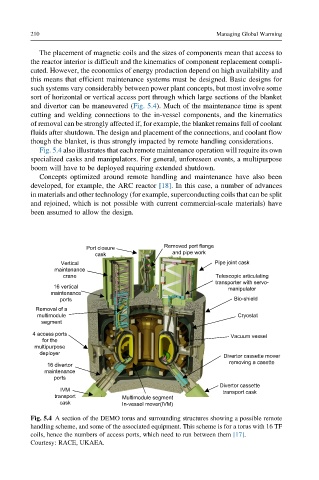
and divertor can be maneuvered (Fig. 5.4). Much of the maintenance time is spent
cutting and welding connections to the in-vessel components, and the kinematics
of removal can be strongly affected if, for example, the blanket remains full of coolant
fluids after shutdown. The design and placement of the connections, and coolant flow
though the blanket, is thus strongly impacted by remote handling considerations.
Fig. 5.4 also illustrates that each remote maintenance operation will require its own
specialized casks and manipulators. For general, unforeseen events, a multipurpose
boom will have to be deployed requiring extended shutdown.
Concepts optimized around remote handling and maintenance have also been
developed, for example, the ARC reactor [18]. In this case, a number of advances
in materials and other technology (for example, superconducting coils that can be split
and rejoined, which is not possible with current commercial-scale materials) have
been assumed to allow the design.
Removed port flange
Port closure
and pipe work
cask
Vertical Pipe joint cask
maintenance
crane Telescopic articulating
transporter with servo-
16 vertical
manipulator
maintenance
ports Bio-shield
Removal of a
multimodule Cryostat
segment
4 access ports
Vacuum vessel
for the
multipurpose
deployer
Divertor cassette mover
removing a casette
16 divertor
maintenance
ports
Divertor cassette
IVM transport cask
transport Multimodule segment
cask In-vessel mover(IVM)
Fig. 5.4 A section of the DEMO torus and surrounding structures showing a possible remote
handling scheme, and some of the associated equipment. This scheme is for a torus with 16 TF
coils, hence the numbers of access ports, which need to run between them [17].
Courtesy: RACE, UKAEA.