Page 156 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 156
Section 5.4 Continuous Casting
Electric furnace
l Tumdish
Platform; 20 m
above ground level
Cooling water Argon
X ray receiver //’ » .
Xqay (Controls pouring rate)
Molten metal
Solidified metal
Air gap Top belt (carbon steel)
TUf1diSh High-velocity
Catch basin Backup rolls cooling waterjets
r
Pinch rolls -_ T GFISIOVI
P“"eY
W” '° ~° ~= - e 3
Nip pulley
Synchronized
`ncn Il
Water nozzle pI ro S
Bottom
Starting dummy OXVQGU |3009 Edge dam blocks belt Water gutters
(for cutting)
(H) (D)
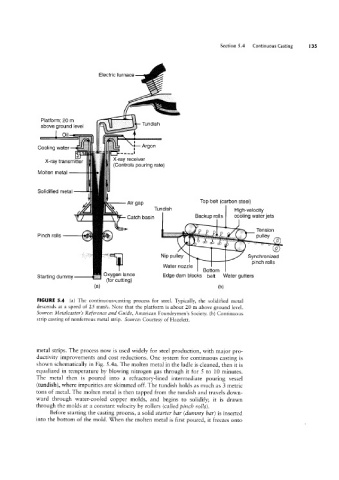
FIGURE 5.4 (a) The continuous-casting process for steel. Typically, the solidified metal
descends at a speed of 25 mm/s. Note that the platform is about 20 m above ground level.
Source: Metalcasterls Reference and Guide, American Foundrymen’s Society. (b) Continuous
strip casting of nonferrous metal strip. Source: Courtesy of Hazelett.
metal strips. The process novv is used widely for steel production, with major pro-
ductivity improvements and cost reductions. One system for continuous casting is
shown schematically in Pig. 5 .4a. The molten metal in the ladle is cleaned, then it is
equalized in temperature by blowing nitrogen gas through it for 5 to 10 minutes.
The metal then is poured into a refractory-lined intermediate pouring vessel
(tundish), where impurities are skimmed off. The tundish holds as much as 3 metric
tons of metal. The molten metal is then tapped from the tundish and travels down-
ward through vvater-cooled copper molds, and begins to solidify; it is drawn
through the molds at a constant velocity by rollers (called pinch rolls).
Before starting the casting process, a solid starter bar (dummy bar) is inserted
into the bottom of the mold. When the molten metal is first poured, it freezes onto