Page 193 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 193
Chapter 7 Polymers: Structure. General Properties, and Applications
military aircraft, sporting goods, toys, appliances, and office equipment. These substi-
tutions reflect the advantages of polymers in terms of the following characteristics:
° Relatively lovv cost (see Table 6.1) and ease of manufacture
° Corrosion resistance and resistance to chemicals
° Low electrical and thermal conductivity
° Lovv density
° High strength-to-Weight ratio (particularly when reinforced)
° Noise reduction
° Wide choice of colors and transparencies
° Ease of manufacturing and complexity of design possibilities
° Other characteristics that may or may not be desirable (depending on the applica-
tion), such as low strength and stiffness (Table 7.1), high coefficient of thermal
expansion, low useful-temperature range-up to about 350°C-and lower di-
mensional stability in service over a period of time.
The Word plastic is from the Greek vvord plastilzos, meaning “capable of being
molded and shaped.” Plastics can be formed, machined, cast, and joined into vari-
ous shapes With relative ease. Minimal additional surface-finishing operations, if
any at all, are required; this characteristic provides an important advantage over
metals. Plastics are available commercially as film, sheet, plate, rods, and tubing of
various cross-sections.
The earliest polymers were made of natural organic materials from animal and
vegetable products; cellulose is the most common example. By means of various
chemical reactions, cellulose is modified into cellulose acetate, used in making sheets
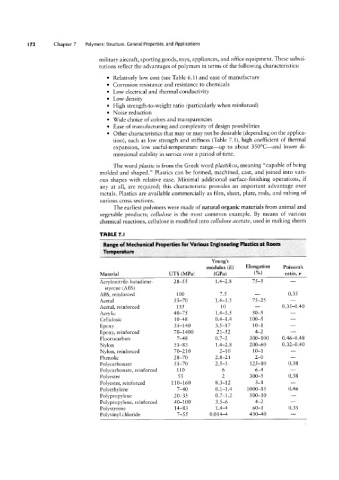
TABLE 1.|
Range of Mechanical Properties for Various Engineering Plastics at Room
Temperature
Young’s
modulus (E) Elongation Poisson’s
Material UTS (MPa) (GPa) l%l ratio, 1/
-
Acrylonitrile-butadiene- 28-55 1.4-2.8 75-5
styrene (ABS) -
-
ABS, reinforced 100 7.5 0.35
-
Acetal 5 5-70 1.4-3.5 75-25
-
Acetal, reinforced 135 10 0.35-0.40
Acrylic 40-75 1.4-3.5 5 0-5 -
Cellulosic 10-48 0.4-1.4 100-5 -
Epoxy 35-140 3.5-17 10-1 -
Epoxy, reinforced 70-1400 21-52 4-2
Fluorocarbon 7-48 0.7-2 300-100 0.46-0.48
-
Nylon 55-83 1.4-2.8 200-60 0.32-0.40
Nylon, reinforced 70-210 2-10 10-1 -
Phenolic 28-70 2.8-21 2-0
Polycarbonate 55-70 2.5-3 125-10 0.38
-
Polycarbonate, reinforced 110 6 6-4
-
Polyester 55 2 300-5 0.38
Polyester, reinforced 1 10-160 8.3-12 3-1
Polyethylene 7-40 0.1-1.4 1000-15 0.46
-
Polypropylene 20-35 0.7-1.2 500-10 _
Polypropylene, reinforced 40-100 3.5-6 4-2
-
Polystyrene 14-83 1.4-4 60-1 0.35
Polyvinyl chloride 7-55 0.014-4 450-40