Page 259 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 259
238 Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Metal Casting
it affects the rate of cooling. The chapter finishes with a description of the factors
influencing defect formation.
Industrial metal-casting processes, design considerations, and casting materials
are described in Chapters 11 and 12. The casting of ceramics and of plastics, which
involves methods and procedures somewhat similar to those for metal, are described
in Chapters 18 and 19, respectively.
|0.2 Solidification of Metals
After molten metal is poured into a mold, a series of events takes place during the
solidification of the metal and its cooling to ambient temperature. These events
greatly influence the size, shape, uniformity, and chemical composition of the grains
formed throughout the casting, which in turn influence the overall properties of the
metal. The significant factors affecting these events are the type of metal, the ther-
mal properties of both the metal and the mold, the geometric relationship between
volume and surface area of the casting, and the shape of the mold.
l0.2.l Pure Metals
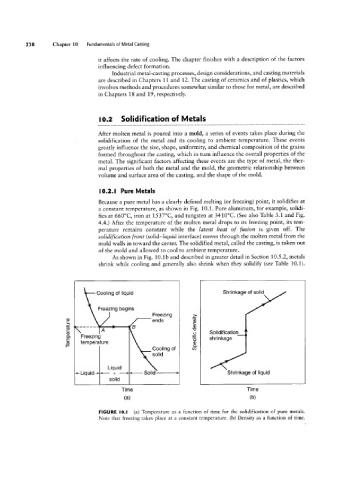
Because a pure metal has a clearly defined melting (or freezing) point, it solidifies at
a constant temperature, as shown in Fig. 10.1. Pure aluminum, for example, solidi-
fies at 660°C, iron at 1537°C, and tungsten at 3410°C. (See also Table 3.1 and Fig.
4.4.) After the temperature of the molten metal drops to its freezing point, its tem-
perature remains constant while the latent heat of fusion is given off. The
solidi/Qcation front (solid-liquid interface) moves through the molten metal from the
mold walls in toward the center. The solidified metal, called the casting, is taken out
of the mold and allowed to cool to ambient temperature.
As shown in Fig. 10.1b and described in greater detail in Section 10.5 .2, metals
shrink while cooling and generally also shrink when they solidify (see Table 10.1).
Cooling of liquid Shrinkage of solid
Freezing begins
Freezing 3.
U.) ends
_
3 _____ B q)
\FreeZingA Z Solidification
temperature 123; Shrinkage
Cooling of cn
solid
Liquid
<-Liquid + Solid > Shrinkage of liquid
solid
Time Time
(H) lb)
FIGURE |0.l (a) Temperature as a function of time for the solidification of pure metals.
Note that freezing takes place at a constant temperature. (b) Density as a function of time.
Temperat