Page 59 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 59
Part I Fundamentals of Materials: Their Behavior and Manufacturing Properties
hard (hence scratch resistant), easy to shape, and easy to clean. Numerous similar
observations can be made about each component of an automobile, ranging from
small screws to wheels. In recent years, fuel economy and the need for improved
performance have driven the substitution of materials, such as aluminum, magne-
sium, and plastics for steel, and the use of composite materials for structural (load-
bearing) components.
As stated in the General Introduction, the selection of materials for individual
components in a product requires a thorough understanding of their properties, func-
tions, and manufacturing costs. A typical automobile is an assemblage of some
15,000 parts; consequently, by saving just one cent on the cost per part, such as by se-
lecting a different material or manufacturing process, the cost of an automobile
would be reduced by $150. The task of engineers thus becomes very challenging,
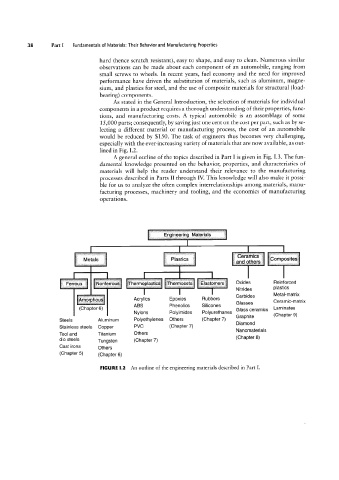
especially with the ever-increasing variety of materials that are now available, as out-
lined in Fig. I.2.
A general outline of the topics described in Part I is given in Fig. I.3. The fun-
damental knowledge presented on the behavior, properties, and characteristics of
materials will help the reader understand their relevance to the manufacturing
processes described in Parts II through IV. This knowledge will also make it possi-
ble for us to analyze the often complex interrelationships among materials, manu-
facturing processes, machinery and tooling, and the economics of manufacturing
operations.
!
,,s.,Xa,<.§];~a\,/2,..,,, J
aa .~f= J,:,a;;.r »f<.
-,n ,f,. sc, ts, ,.,.-. /.;_,; ...~
Metal-mat
f » - -. ;ce,:s..,,gaa_.@[Aa~<.,esc=cs;..; .....<:._ac.,.Qs_i;;;.;,s.~y\./s, oxides Reinforced
Acrylics Epoxies Rubbers gT;;’;;(;S Ceramic_n:l;mX
(Chapter 6) ABS Phenolics Silicones Glass Ceramics Laminates
Nylons Polyimides Polyurethanes (Chapter 9)
Stee|S Aluminum Polyethylenes Others (Chapter 7) gfapmt;
Stainless steels Copper PVC (ChaDl@f7) Nlamont
Tool and Titanium Others anoma ella S
die Steels Tungsten (Cl1aPl9f 7) (Chapter 8)
Cast irons Others
(Chapter 5) (Chapter 6)
FIGURE l.2 An outline of the engineering materials described in Part I.