Page 613 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 613
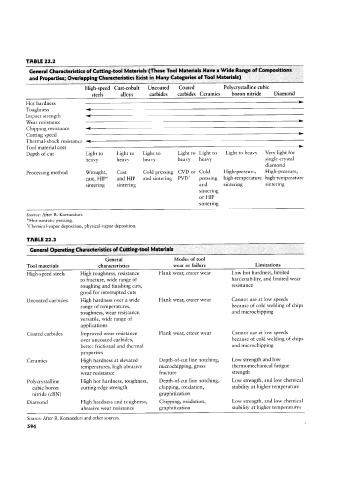
TABLE 22.2
General Characteristics of Cutting-tool Materials (These Tool Materials Have a Wide Range nf Compositions
and Properties; Overlapping Characteristics Exist in Many Categories of Tool Materials)
High-speed Cast-cobalt Uncoated Coated Polycrystalline cubic
steels alloys carbides carbides Ceramics boron nitride Diamond
>
Hot hardness
Toughness 4
Impact strength 4
Wear resistance >
Chipping resistance 4
Cutting speed >
Thermal-shock resistance 4
Tool material cost >
Depth of cut Light to Light to Light to Light to Light to Light to heavy Very light for
heavy heavy heavy heavy heavy single-crystal
diamond
Processing method Wrought, Cast Cold pressing CVD or Cold High-pressure, High-pressure,
cast, HIP* and HIP and sintering PVDI pressing high-temperature high-temperature
sintering sintering and sintering sintering
sintering
or HIP
sintering
Source: After R. Komanduri.
"Hot~isostatic pressing.
lChemical-vapor deposition, physical-vapor deposition.
TABLE 22.3
General Operating Characteristics of Cutting-tool Materials
General Modes of tool
Tool materials characteristics wear or failure Limitations
High-speed steels High toughness, resistance Flank Wear, crater wear Low hot hardness, limited
to fracture, wide range of hardenability, and limited wear
roughing and finishing cuts, resistance
good for interrupted cuts
Uncoated carbides High hardness over a wide Flank Wear, crater Wear Cannot use at low speeds
range of temperatures, because of cold Welding of chips
toughness, Wear resistance, and microchipping
versatile, wide range of
applications
Coated carbides Improved Wear resistance Flank Wear, crater Wear Cannot use at low speeds
over uncoated carbides, because of cold Welding of chips
better frictional and thermal and microchipping
properties
Ceramics High hardness at elevated Depth-of-cut line notching, Low strength and low
temperatures, high abrasive microchipping, gross thermomechanical fatigue
Wear resistance fracture strength
Polycrystalline High hot hardness, toughness, Depth-of-cut line notching, Low strength, and low chemical
cubic boron cutting-edge strength chipping, oxidation, stability at higher temperature
nitride (CBN) graphitization
Diamond High hardness and toughness, Chipping, oxidation, Low strength, and low chemical
abrasive wear resistance graphitization stability at higher temperatures
Source: After R. Komanduri and other sources.
594