Page 69 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 69
Chapter 1 The Structure of Metals
Note in Fig. 1.10d that the growing grains eventually interfere with and im-
pinge upon one another. The surfaces that separate these individual grains are called
grain boundaries. Note also that the crystallographic orientation changes abruptly
from one grain to the next across the grain boundaries. (Recall, from Section 1.4,
that the behavior of a single crystal or a single grain is anisotropic.) Thus, because
its many grains have random crystallographic orientations, the behavior of a piece
of polycrystalline metal is essentially isotropic; that is, its properties do not vary
with the direction of testing.
l.5.l Grain Size
Grain size has a major influence on the mechanical properties of metals. At room
temperature, for example, a large grain size is generally associated with low
strength, low hardness, and low ductility. Grains can be so large as to be visible with
the naked eye; zinc grains on the surface of galvanized sheet steels are an example.
Large grains also cause a rough surface appearance after the material has been plas-
tically deformed, particularly in the stretching of sheet metals (see orange peel,
Section 1.7).
Grain size is usually measured by counting the number of grains in a given
area, or by counting the number of grains that intersect a length of a line randomly
drawn on an enlarged photograph of the grains (taken under a microscope on a pol-
ished and etched specimen). Grain size may also be determined by comparing such a
photograph against a standard chart.
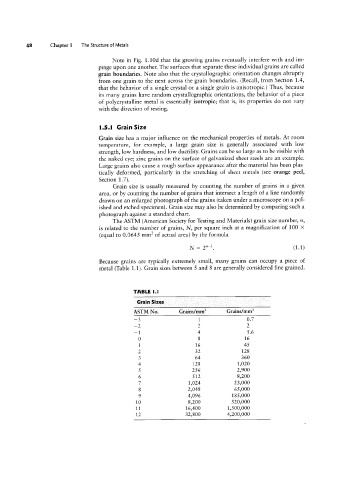
The ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) grain size number, n,
is related to the number of grains, N, per square inch at a magnification of 100 ><
(equal to 0.0645 mmf of actual area) by the formula
N = 2"T1. (1.1)
Because grains are typically extremely small, many grains can occupy a piece of
metal (Table 1.1). Grain sizes between 5 and 8 are generally considered fine grained.
TABLE l.l
Grain Sizes
ASTM No. Grains/mmz Grains/mm3
-3 1 0 7
-2 2 2
A1 4 5 6
0 8 16
1 16 45
2 32 128
3 64 360
4 128 1,020
5 256 2,900
6 512 8,200
7 1,024 23,000
8 2,048 65,000
9 4,096 185,000
10 8,200 520,000
11 16,400 1,500,000
12 32,800 4,200,000