Page 227 - Marine Structural Design
P. 227
Chapter1 0 Ultimate Strength of Plates and Stiffened Plates 203
structural deterioration are present, it is recommended that additional strength analyses by
more refined methods be performed to derive reduction factors.
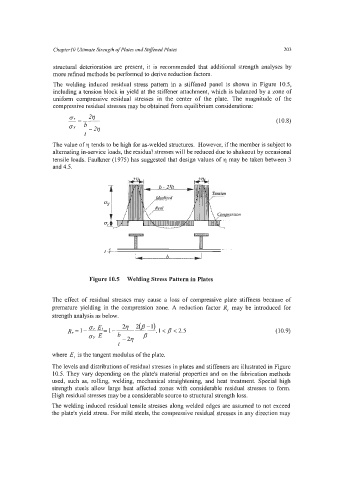
The welding induced residual stress pattern in a stiffened panel is shown in Figure 10.5,
including a tension block in yield at the stiffener attachment, which is balanced by a zone of
uniform compressive residual stresses in the center of the plate. The magnitude of the
compressive residual stresses may be obtained from equilibrium considerations:
-=- 27 (10.8)
cr
cy b-z7
t
The value of q tends to be high for as-welded structures. However, if the member is subject to
alternating in-service loads, the residual stresses will be reduced due to shakeout by occasional
tensile loads. Faulkner (1975) has suggested that design values of q may be taken between 3
and 4.5.
t
Figure 10.5 Welding Stress Pattern in Plates
The effect of residual stresses may cause a loss of compressive plate stiffness because of
premature yielding in the compression zone. A reduction factor R, may be introduced for
strength analysis as below.
(10.9)
where E, is the tangent modulus of the plate.
The levels and distributions of residual stresses in plates and stiffeners are illustrated in Figure
10.5. They vary depending on the plate's material properties and on the fabrication methods
used, such as, rolling, welding, mechanical straightening, and heat treatment. Special high
strength steels allow large heat affected zones with considerable residual stresses to form.
High residual stresses may be a considerable source to structural strength loss.
The welding induced residual tensile stresses along welded edges are assumed to not exceed
the plate's yield stress. For mild steels, the compressive residual stresses in any direction may