Page 442 - Marine Structural Design
P. 442
418 Part IY Structural Reliability
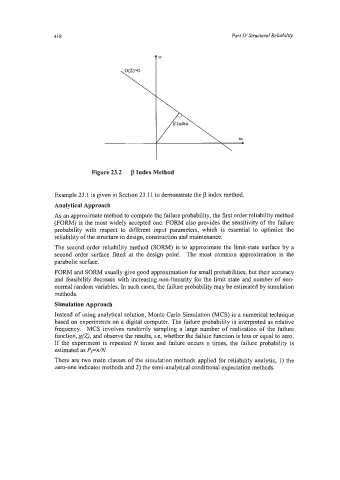
Figure 23.2 j3 Index Method
Example 23.1 is given in Section 23.11 to demonstrate the j3 index method.
Analytical Approach
As an approximate method to compute the failure probability, the first order reliability method
(FORM) is the most widely accepted one. FORM also provides the sensitivity of the failure
probability with respect to different input parameters, which is essential to optimize the
reliability of the structure in design, construction and maintenance.
The second order reliability method (SORM) is to approximate the limit-state surface by a
second order surface fitted at the design point. The most common approximation is the
parabolic surface.
FORM and SORM usually give good approximation for small probabilities, but their accuracy
and feasibility decrease with increasing non-linearity for the limit state and number of non-
normal random variables. In such cases, the failure probability may be estimated by simulation
methods.
Simulation Approach
Instead of using analytical solution, Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) is a numerical technique
based on experiments on a digital computer. The failure probability is interpreted as relative
frequency. MCS involves randomly sampling a large number of realization of the failure
function, gp), and observe the results, i.e, whether the failure function is less or equal to zero.
If the experiment is repeated N times and failure occurs n times, the failure probability is
estimated as PFnhV.
There are two main classes of the simulation methods applied for reliability analysis, 1) the
zero-one indicator methods and 2) the semi-analytical conditional expectation methods.