Page 507 - Marine Structural Design
P. 507
Chapter 27 Fatigue Reliability 483
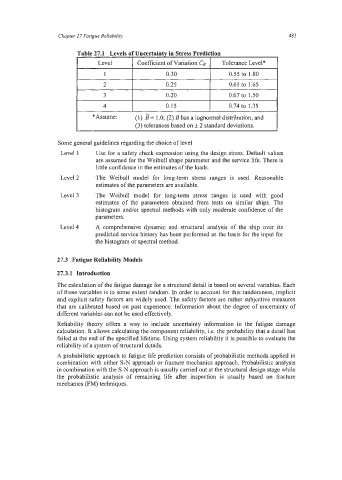
2 0.25 0.61 to 1.65
3 0.20 0.67 to 1.50
4 0.15 0.74 to 1.35
Some general guidelines regarding the choice of level
Level 1 Use for a safety check expression using the design stress. Default values
are assumed for the Weibull shape parameter and the service life. There is
little confidence in the estimates of the loads.
Level 2 The Weibull model for long-term stress ranges is used. Reasonable
estimates of the parameters are available.
Level 3 The Weibull model for long-term stress ranges is used with good
estimates of the parameters obtained from tests on similar ships. The
histogram and/or spectral methods with only moderate confidence of the
parameters.
Level 4 A comprehensive dynamic and structural analysis of the ship over its
predicted service history has been performed as the basis for the input for
the histogram or spectral method.
27.3 Fatigue Reliability Models
27.3.1 Introduction
The calculation of the fatigue damage for a structural detail is based on several variables. Each
of these variables is to some extent random. In order to account for this randomness, implicit
and explicit safety factors are widely used. The safety factors are rather subjective measures
that are calibrated based on past experience. Information about the degree of uncertainty of
different variables can not be used effectively.
Reliability theory offers a way to include uncertainty information in the fatigue damage
calculation. It allows calculating the component reliability, i.e. the probability that a detail has
failed at the end of the specified lifetime. Using system reliability it is possible to evaluate the
reliability of a system of structural details.
A probabilistic approach to fatigue life prediction consists of probabilistic methods applied in
combination with either S-N approach or fracture mechanics approach. Probabilistic analysis
in combination with the S-N approach is usually carried out at the structural design stage while
the probabilistic analysis of remaining life after inspection is usually based on fracture
mechanics (FM) techniques.