Page 554 - Marine Structural Design
P. 554
530 Part V Risk Assessment
30.2 Collision Risk
The ship/platform collision is one of the main risk contributors in the offshore exploration and
production activities. The most frequently occurred collisions are impacts between offshore
supply vessels and platforms. In most situations this type of collisions only causes minor
damage to the platforms.
30.2.1 Colliding Vessel Categories
The first step in evaluating the collision risk is to specify the different types of vessels that
may collide with an offshore platform. Collision hazards due to the field related supply vessels
are characterized with high frequency and low consequence. The passing vessels may lose
their power and drift resulting in collisions with the platforms. In the North Sea, merchant
vessels represent the greatest hazard, since they are often large and thus have considerable
impact energy in a collision with the platforms. Further, in some areas the merchant traffic can
be very busy. Table 30.1 summarizes the colliding vessel categories, based on information in
Vinnem (1999). In the following Sections, only the external passing vessel collision is
evaluated.
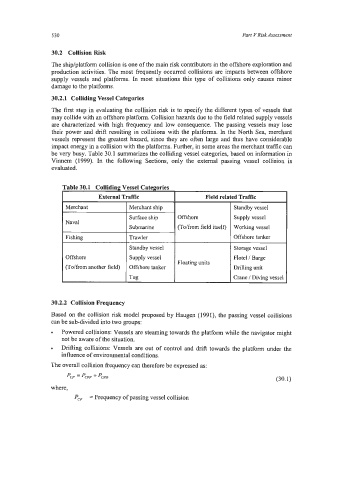
rable 30.1 Colliding Vessel Categories
External Traffic Field related Traffic
Merchant I Merchant ship Standby vessel
Surface ship Offshore Supply vessel
Naval
Submarine (To/from field itself) Working vessel
Fishing I Trawler Offshore tanker
Standby vessel Storage vessel
Offshore Supply vessel Flotel / Barge
Floating units
(Tolfrom another field) Offshore tanker Drilling unit
Tug
30.2.2 Collision Frequency
Based on the collision risk model proposed by Haugen (1991), the passing vessel collisions
can be sub-divided into two groups:
Powered collisions: Vessels are steaming towards the platform while the navigator might
not be aware of the situation.
Drifting collisions: Vessels are out of control and drift towards the platform under the
influence of environmental conditions.
The overall collision frequency can therefore be expressed as:
PCP = PCPP -I- PCPD (30.1)
where,
PCp = Frequency of passing vessel collision