Page 64 - Marine Structural Design
P. 64
Chapter 3 Loah and Dynamic Response for qffshore Structures 41
Loop and eddy currents
16 __ -1 year -
//--
....... IO years
12 - - -- 100 yea’s
....... ...
4-
... .. ...
07
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Spectral peak period, T,
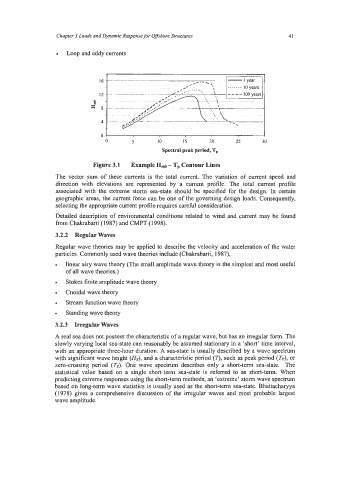
Figure 3.1 Example H,,,o - Tp Contour Lines
The vector sum of these currents is the total current. The variation of current speed and
direction with elevations are represented by a current profile. The total current profile
associated with the extreme storm sea-state should be specified for the design. In certain
geographic areas, the current force can be one of the governing design loads. Consequently,
selecting the appropriate current profile requires careful consideration.
Detailed description of environmental conditions related to wind and current may be found
from Chakrabarti (1987) and CMPT (1998).
3.2.2 Regular Waves
Regular wave theories may be applied to describe the velocity and acceleration of the water
particles. Commonly used wave theories include (Chakrabarti, 1987),
linear airy wave theory (The small amplitude wave theory is the simplest and most useful
0
of all wave theories.)
Stokes finite amplitude wave theory
Cnoidal wave theory
Stream function wave theory
Standing wave theory
0
3.2.3 Irregular Waves
A real sea does not possess the characteristic of a regular wave, but has an irregular form. The
slowly varying local sea-state can reasonably be assumed stationary in a ‘short’ time interval,
with an appropriate three-hour duration. A sea-state is usually described by a wave spectrum
with significant wave height (Hs), and a characteristic period (T), such as peak period (Tp), or
zero-crossing period (T’). One wave spectrum describes only a short-term sea-state. The
statistical value based on a single short-term sea-state is referred to as short-term. When
predicting extreme responses using the short-term methods, an ‘extreme’ storm wave spectrum
based on long-term wave statistics is usually used as the short-term sea-state. Bhattacharyya
(1 978) gives a comprehensive discussion of the irregular waves and most probable largest
wave amplitude.