Page 143 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 143
where MFP =
mean free path
V =
3
volume of the space, ft or m 3
S =
2
surface area of the space, ft or m 2
For example, in a room measuring 25 × 20 × 10 ft, on average a sound travels a distance of 10.5 ft
between reflections. Sound travels 1.13 ft/msec. At that speed it takes 9.3 msec to traverse the mean-
free distance of 10.5 ft. Viewed another way, about 107 reflections take place in the space of a
second.
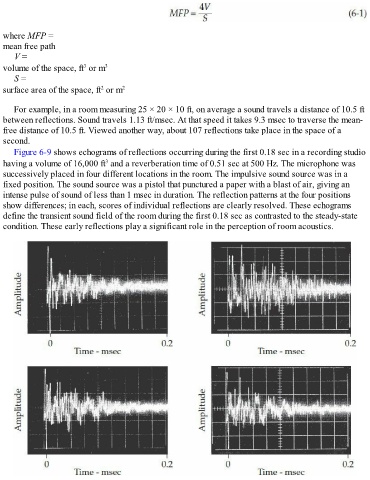
Figure 6-9 shows echograms of reflections occurring during the first 0.18 sec in a recording studio
3
having a volume of 16,000 ft and a reverberation time of 0.51 sec at 500 Hz. The microphone was
successively placed in four different locations in the room. The impulsive sound source was in a
fixed position. The sound source was a pistol that punctured a paper with a blast of air, giving an
intense pulse of sound of less than 1 msec in duration. The reflection patterns at the four positions
show differences; in each, scores of individual reflections are clearly resolved. These echograms
define the transient sound field of the room during the first 0.18 sec as contrasted to the steady-state
condition. These early reflections play a significant role in the perception of room acoustics.