Page 207 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 207
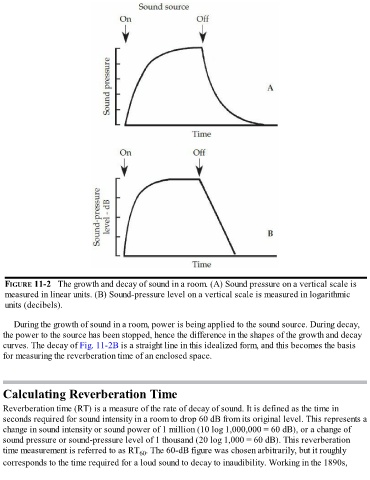
FIGURE 11-2 The growth and decay of sound in a room. (A) Sound pressure on a vertical scale is
measured in linear units. (B) Sound-pressure level on a vertical scale is measured in logarithmic
units (decibels).
During the growth of sound in a room, power is being applied to the sound source. During decay,
the power to the source has been stopped, hence the difference in the shapes of the growth and decay
curves. The decay of Fig. 11-2B is a straight line in this idealized form, and this becomes the basis
for measuring the reverberation time of an enclosed space.
Calculating Reverberation Time
Reverberation time (RT) is a measure of the rate of decay of sound. It is defined as the time in
seconds required for sound intensity in a room to drop 60 dB from its original level. This represents a
change in sound intensity or sound power of 1 million (10 log 1,000,000 = 60 dB), or a change of
sound pressure or sound-pressure level of 1 thousand (20 log 1,000 = 60 dB). This reverberation
time measurement is referred to as RT . The 60-dB figure was chosen arbitrarily, but it roughly
60
corresponds to the time required for a loud sound to decay to inaudibility. Working in the 1890s,