Page 205 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 205
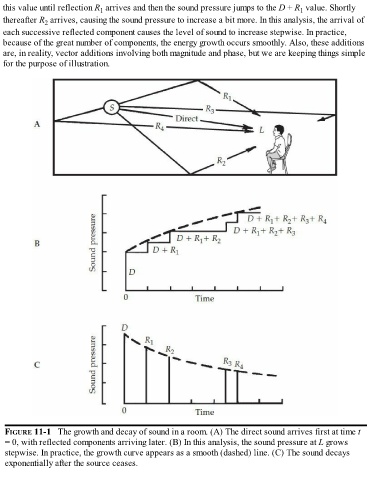
this value until reflection R arrives and then the sound pressure jumps to the D + R value. Shortly
1
1
thereafter R arrives, causing the sound pressure to increase a bit more. In this analysis, the arrival of
2
each successive reflected component causes the level of sound to increase stepwise. In practice,
because of the great number of components, the energy growth occurs smoothly. Also, these additions
are, in reality, vector additions involving both magnitude and phase, but we are keeping things simple
for the purpose of illustration.
FIGURE 11-1 The growth and decay of sound in a room. (A) The direct sound arrives first at time t
= 0, with reflected components arriving later. (B) In this analysis, the sound pressure at L grows
stepwise. In practice, the growth curve appears as a smooth (dashed) line. (C) The sound decays
exponentially after the source ceases.