Page 256 - Master Handbook of Acoustics
P. 256
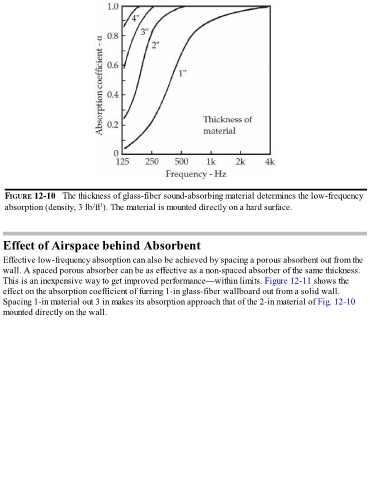
FIGURE 12-10 The thickness of glass-fiber sound-absorbing material determines the low-frequency
3
absorption (density, 3 lb/ft ). The material is mounted directly on a hard surface.
Effect of Airspace behind Absorbent
Effective low-frequency absorption can also be achieved by spacing a porous absorbent out from the
wall. A spaced porous absorber can be as effective as a non-spaced absorber of the same thickness.
This is an inexpensive way to get improved performance—within limits. Figure 12-11 shows the
effect on the absorption coefficient of furring 1-in glass-fiber wallboard out from a solid wall.
Spacing 1-in material out 3 in makes its absorption approach that of the 2-in material of Fig. 12-10
mounted directly on the wall.